RECENT
IS HGH AN EFFECTIVE ANTI-AGING DRUG?
Growth Hormone (GH) has been shown to offset many of the side effects of aging. Supplementation can reduce body fat, increase lean muscle, improve skin elasticity, energy and sex drive. Many claim GH is a »fountain of youth«. However several studies point to a significant potential downside - increased GH levels may reduce lifespan. In this article we will discuss the latest findings and the pros and cons of GH supplementation for anti-aging.
Growth Hormone (GH) has been shown to offset many of the side effects of aging. Supplementation can reduce body fat, increase lean muscle, improve skin elasticity, energy and sex drive. Many claim GH is a “fountain of youth”. However several studies point to a significant potential downside - increased GH levels may reduce lifespan. In this article we will discuss the latest findings and the pros and cons of GH supplementation for anti-aging.
WHAT IS A HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE?
HGH or GH is a hormone produced by the pea-sized pituitary gland that is located at the base of our brains. In the early stages of our lives it fuels growth, it also helps maintain tissues and organs throughout life.
WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF GROWTH HORMONE?
GH stimulates body growth by stimulating the liver and other tissues to secrete IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor). IGF-1 is anabolic - it increases lean muscle mass and reduces fat tissue simultaneously. It also promotes neurogenesis which is the growth of new brain cells and has neuroprotective properties – it prevents brain cells from dying.
However, as we age there is a natural slowdown in GH production and consequently IGF-1. This can lead to muscle wasting, loss in bone density, reduced skin elasticity, increased fat retention, loss of immune function and cognitive decline – many of the signs we associate with aging.
Many people supplement synthetic GH to prevent some of the side effects of aging. HGH promoties muscle, bone growth and also slows down apoptosis. Apoptosis is a programmed cell death that protects against the spreading of infectious diseases and cancer, but it can also lead to the death of healthy cells as we get older. GH also promotes new nerve growth in the brain which can lead to better cognitive performance and wellbeing (1) (2).
WHAT EFFFECT DOES IT HAVE ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM?
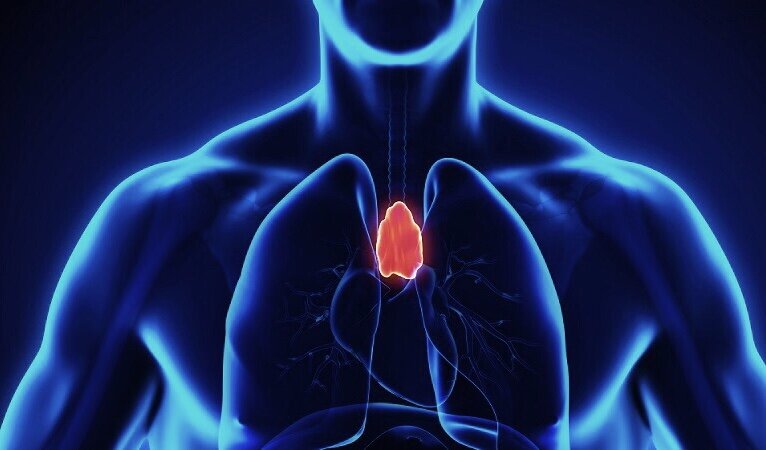
Our immune systems deterioate with age. One of the organs responsible for our immune system to function properly is thymus – this is the primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within lymphoid organs T-cells mature. T-cells are type of white blood cells that are essential part of our immune system. They determine the specificity of immune response to foreign substances in the body or in other words – antigens.
The thymus is fully developed by the time we are 10 years old but then it starts shrinking. This gradual shrinking is related to the decline in our immune systems as we get older.
So called thymic involution (the shrinking of the thymus with age) leads to growing mortality risk, decrease in tissue mass and depletion of critical immune cell populations. That is linked to age-related increases in cancer incidence, infectious diseases, autoimmune conditions, generalized inflammation and atherosclerosis (3).
Supplementation with GH has been shown to help rejuvinate the Thymus and therefore boost our immune systems.
THREE-DRUG COMBINATION TO BOOST THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
From 2015-2017 a human clinical trial was conducted in attempt to reverse various aspects of human aging. It was called TRIIM (Thymus Regeneration, Immunorestoration, Insulin Mitigation). In this trial they used growth hormone to reverse biological aging of the immune system in a population of 51 to 65 year old healthy men.
GH is known to increase blood sugar levels so they used combined GH with DHEA and metformin to keep blood sugar levels in check. Metformin is used to treat people with type 2 diabetes and has been proposed as a candidate for slowing aging in humans before. All of the mentioned drugs (GH, DHEA, metformin) have been linked to slowing the aging process in the laboratory (4).
During the trial the composition of thymus was checked and blood samples were taken to analyze immune cell counts. The trial's results were impressive, the patients Thymus' appeared to regenerate, fat tissue was replaced with regenerated, healthy tissue. Not only that, the parcipants' biological age was 1.5 years lower than when they first entered the trial! The sample size in this study was small but the results were very consistent
What is interesting is that this study showed that supplementing with GH for a relatively short time period led to a rejuvination of the thymus. Other studies have demonstrated similar results, short term supplementation such as 6 months can lead to significant changes in our organs, winding back the body clock by years (5).
SO WHAT IS THE DOWNSIDE?
While GH may help you to feel and look younger, increased levels of GH (or more specifically IGF-1) has been linked to shorter lifespan. This has led to a great deal of confusion in the anti-aging community, is GH a fountain of youth, or a potential accelerant of the aging process?
In experiments in mice, worms and flies the subjects with lower levels of GH lived longer. Mice with GH and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) deficiencies lived 50 % longer than mice of the same species with no deficiencies. It appears GH or at least IGF-1 promotes growth but also depresses life span across many species (6). In humans decreased IGF-1 is in fact correlated with the longevity of centenarians (people who has reached the age of 100 years).
Elevated levels of circulating IGF-1 might decrease lifespan because IGF-1 causes increased cell proliferation which can raise our suceptibility to diseases such as cancer (7). Too much of human growth hormone can also cause arthritis, diabetes and even heart failure.
Reduced growth hormone and IGF-1 may also increase lifespan by increasing the expresion of genes that are involved in stress resistance and DNA repair.
However, we should be wary, the reduction of IGF-1 expression levels can come at an expensive cost especially when it comes to muscle and brain maintenance and repair. Results from various studies have been very inconsistent (8).
IS IT A TRADE OFF?
Ecologists and other evolutionary biologists have pointed out dozens of trade-offs in natural populations. Perhaps individuals that reproduce (or reproduce more) have a corresponding decrease in some fitness trait such as longevity (9). Evolution may be forced to accept costly tradeoff later in life in exchange for better chances for early individual reproductive success.
IGF-1 is good example of an evolutionary trade off. IGF-1 stimulates rapid growth (tissues and organs growth) and development in early stages of our lives but it can also have some negative long-term effects such as cancer and can increase mortality.
This theory works very well with the counterintuitive findings that most of the »longevity genes« discovered in various organisms are either loss-of-function mutations or mutations that reduced the level of gene expression (8).
The evidence to support this theory is still limited. There is a lot of IGF-1 early in our lives but the effects are not as harmful. Later in life IGF-1 is at very low levels so the correlation between higher levels of IGF-1 in our teens and risk of cancer and other diseases in our older years is very hard to explain.
how can we balance the benefits, while minimizing the risks?
FIRST TRY TO BOOST GH LEVELS NATURALLY
Some scientists claim enhancing GH and IGF the natural way may maximize the benefits without the costs. There are natural and effective ways we can increase natural growth hormone levels:
Strenuous exercise has been shown to increase growth hormone levels
but it is important to mention that we can get acclimated to exercise over
time which will lead to less hormone secretion from glands.
Intense heat stress induces a massive rise in GH - 30 minute sauna
therapy has been shown to cause a rapid boost in growth hormone levels.
A research study from 2007 found that group with a 30 minute
continuous sauna session showed higher elevations in hGH levels (10).
Eat a healthy diet, rich in healthy fats and low in sugar.
Get plenty of sleep.
DON'T GO CRAZY
If you choose to supplement with GH, make sure you see a doctor and get your blood tested first. Supplementation with exogenous GH is only recommended for people who are unable to boost their GH to healthy levels using the natural methods described above.
Supplementation is usually only considered for people older than 40, this is when the drop in GH becomes more noticable. If supplementing make sure the dose you take doesn't take your GH levels higher than that of a health 30 year old.
Only supplement for short periods of time (not more than 3 months) and take regular breaks. Supplementing for 3 months once per year should be more than enough to restore the thymus to healthy function. Not taking GH for extended periods will help to reduce the potential negative impact on longevity.
CONCLUSION
Growth hormone supplementation provides many physical and psychological benefits however the correlation between higher GH levels and shorter lifespans is worrying - therefore moderation is advised. Further research with larger and more diverse populations are needed before we will fully understand how to maximise the benefits and minimize the risks. In the meantime try boosting your GH levels naturally, through high intensity training, sauna, a healthy diet and making sure you get plenty of sleep. If you decide to supplement do so only under the supervision of a doctor and not for more than 3 months a year.
REFERENCES
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2682398/
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6305861/
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6276058/
4. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/acel.13028
6. https://academic.oup.com/biomedgerontology/article/67A/6/652/583809
7. Longo, V. D. and L. Fontana. 2010. Caloric restriction and cancer prevention: metabolic and molecular mechanisms. Trends Phamacol. Sci. 31:89-98.
8. https://wjmh.org/DOIx.php?id=10.5534/wjmh.180018
9. Leroi, A. M., A. Bartke, G. D. Benedictis, C. Franceschi, A. Gartner, E. Gonos, M. E. Feder, T. Kivisild, S. Lee, N. Kartal-Ozer, Schumacher, M., Sikora, E., Slagboom, E., Tatar, M., Yashin, A. I., Vijg, J, and B. Zwaan. 2005. What evidence is there for the existence of individuals genes with antagonistic pleiotropic effects ? Mech. Age. Dev. 126:421-429
10. https://journals.indexcopernicus.com/search/article?icid=890538
What is intermittent fasting and what are the benefits?
Intermittent fasting, refers to a diet that involves avoiding food intake, for a period of time, on a regular basis. Intermittent fasting delivers many benefits beyond just weight-loss, it may even help to extend lifespan. In this article we explore what intermittent fasting is, what benefits it can deliver and various methods of practicing this diet.
Intermittent fasting, refers to a diet that involves avoiding food intake, for a period of time, on a regular basis. Intermittent fasting delivers many benefits beyond just weight-loss, it may even help to extend lifespan. In this article we explore what intermittent fasting is, what benefits it can deliver and various methods of practicing this diet.
What is intermittent fasting?
Intermittent fasting is a special diet in which people have to restrict how much or when they eat food in a given period of time. It involves eating food only during a specific number of hours in a day or week.
Intermittent fasting differs from other diets in that it does not tell you what you can or can’t eat, nor how much to eat. During the feeding times you can eat whatever you want, and as much as you want!
There are various methods of intermittent fasting, some lasting hours and some lasting several days, we will go into more detail on the different methods of fasting later in this article.
Typically, during the period of fasting you may not eat any food, however there are exceptions on some longer fasting programs you may be allowed a small amount of calories. During the fasting period you are allowed to drink water, unsweetened tea and coffee, and other low-calorie beverages.
What are the benefits of intermittent fasting?
Promotes longevity
Animal studies have shown that intermittent fasting can significantly extend lifespan. The results are striking, in one study rats who fasted every other day lived 83% longer on average than the control group (1).
While the effect on longevity hasn’t been proven in humans, intermittent fasting has been shown to deliver a range of benefits in humans which should contribute to increased lifespan, these are outlined below.
Promotes weight loss
Obesity is one of the common precursors to several diseases including heart attacks, high cholesterol, stroke, hypertension, and diabetes. These disorders are known to reduce the lifespan of a person and also affect their quality of life.
Intermittent fasting can promote weight loss by triggering the use of fats stored in the body (2).
Intermittent fasting involves eating fewer meals, which reduces the calorie intake of a person. Unless the person compensates for the reduced number of meals by overeating during the phase of food intake (typically you won’t), the overall calorie consumption of a person stands reduced.
Intermittent fasting also causes reduced insulin production, increased growth hormone secretion (up to 5x normal amounts), and increased norepinephrine levels all of which support the breakdown of fats to be used as energy (3) (4).
Fasting is a quick way to lose weight
May help prevent cancer
Fasting slows down the rate of cell growth, and stimulates autophagy, the body’s clean up mode. Both of these effects may help to reduce the growth of cancers, or even eliminate small tumors and pre-cancerous cells. Conclusive human studies are still needed but the results in animals appear promising.
In one study a group of rats were infected with tumors, 50% of those on calorie restriction survived 10 days later, whereas only 13% of those with normal diets survived (5).
In addition, fasting during chemotherapy treatment seems to reduce the side effects of chemotherapy. This works because chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing cells. During fasting cell division slows down, this slowing effect is far more pronounced in regular tissues than in cancer cells. Thus the chemotherapy is able to better target cancer cells while affecting fewer healthy cells (6).
Improves organ and brain health
Intermittent fasting can improve the health of vital organs including the brain, heart, liver, and kidneys, thereby improving longevity. For example; research studies have revealed that intermittent fasting can improve the risk factors for heart attacks such as hypertension, inflammatory markers, cholesterol and triglycerides levels, and blood sugar levels (7).
It can also slow down the degenerative changes in the brain and improve cognitive functions such as memory, attention span, and problem-solving skills. It may reduce the risk of degenerative brain disorders like Alzheimer's disease, and dementia and thus, improve longevity (8).
Fasting can help protect our brains from degenerative diseases like dementia
How else does it benefit longevity, at a cellular level?
Improved cellular clean up processes
Our cells incur a huge amount of DNA damage on a daily basis. This is caused by environmental factors such as solar radiation and pollution, by-products from our metabolism such as free radicals, and the DNA replication itself is prone to error.
Fortunately, our bodies can repair damaged DNA. One method of DNA repair is via the sirtuin proteins. Sirtuins are a family of proteins that assist in DNA repair. They are activated when the body senses it is in a stressed state (e.g. fasting). Activating the sirtuins accelerates the DNA repair processes in our bodies.
Fasting also stimulates a cellular detoxification processes known as autophagy (9). Autophagy is the body's way of cleaning out cellular trash to restore the health and functioning of cells. This cellular trash if left uncleared can lead to inflammation and even cancer.
Every day our DNA incurs millions of DNA strand breaks, which need to be repaired
Improved mitochondrial functions
A research study conducted by Harvard researchers has shown that intermittent fasting could increase lifespan by slowing down degenerative changes in the body and delaying the effects of aging. It is believed to work by improving general health by modifying the activities of the mitochondrial network inside the body cells and tissues (10).
Mitochondria work like small power plants for our cells. Mitochondria also play a key role in the aging of the cells. The studies have shown that changing the shape of mitochondrial networks can enhance the power generating abilities of the cells and thereby improve their longevity and lifespan.
More importantly, it also illustrates that fasting could manipulate these mitochondrial networks and thus, maintain their "youthful" state (11).
Mitochondria are the power factories of our cells
Reduced oxidative stress and inflammation
Oxidative stress and inflammation in the cells can speed up the aging process.
Oxidative stress occurs due to the damage caused by unstable molecules known as free radicals. Free radicals have the ability to react with and damage other molecules such as proteins and DNA. This can trigger degenerative and cancerous changes in healthy organs. Similarly inflammation in the body can cause damage to nearby cells and DNA.
Several studies have shown that intermittent fasting could enhance the body's resistance to free radical damage or oxidative stress and reduce inflammation to slow down aging. It can also reduce the risk of cancer by protecting healthy cells against toxins and carcinogenic agents like free radicals (12).
What method of intermittent fasting seems to be the most effective?
There are several different forms of intermittent fasting, the most common approaches are described below. Ultimately, the best method of fasting is the one which works for you. Choose something you can stick to and incorporate in your routines.
Shorter fasts
Shorter fasts last for less than 24 hours. Shorter fasts are more suitable for people who are new to fasting and are not used to avoiding food intake for prolonged hours. Shorter fasts still deliver a range of benefits and can be easier to incorporate into your weekly habits.
There are two common approaches, the 16:8 and the 20:4.
In 16:8 intermittent fasting, the person should fast every day for 16 hours continuously. Sometimes, it is also called the 8-hour eating ‘window’ method. All meals should be consumed within the 8-hour time period. The 8-hour time period needs to be continuous and cannot be broken down into two or more phases.
For the rest of the 16 hours of each day you should not consume any calories. This method can be followed safely every day.
An example of 16:8 is eating all your food between 11:00 am and 7:00 pm. This would require you to skip breakfast and have an early dinner. You can eat 2 or 3 meals during the 8-hour period. You can also choose any continuous time period of 8 hours to eat depending on your routine or personal preferences.
20:4 is another form of short fasting method that involves a 4-hour window for eating and a 20-hour window for fasting. You can choose a continuous time period of 4 hours such as between 1:00 pm and 5:00 pm every day and avoid food intake for the remaining 20 hours. This would generally involve eating 1 meal or 2 smaller meals within the 4-hour period.
Shorter fasts need to be done more frequently in order to derive the expected health benefits.
24-hour fasts
A longer fast of 24 hours can be adopted by those who feel they have the capacity to go without food for a longer duration. We suggest you try a couple of shorter fasts first before working your way up to a 24-hour fast.
The 24-hour intermittent fasting involves avoiding food intake from lunch to lunch or dinner to dinner. For example; you can eat dinner on the first day, , skip breakfast and lunch the next day, then eat dinner. This form of intermittent fasting is usually done 1 to 3 times per week.
The 5:2 intermittent fasting approach is a popular form of the 24 hour fast. The 5:2 approach involves fasting for 24 hours 2 times per week, on the other 5 days you can eat normally.
Alternate-day fasting is another common approach to the 24 hour fast whereby a person fasts for 24 hours every second day. During the other days they can eat normally.
Extended fasting
This form of intermittent fasting lasts for more than 24 hours. Extended fasting is recommended only for people who have some experience with fasting and are already comfortable fasting for 24 hours. Anyone considering extended fasting should consult their doctor first to ensure they would not be at any risk while fasting.
Extended fasting involves avoiding food intake for 2 to 14 days. Fasting for more than 14 days is not advisable as it can increase the risk of refeeding syndrome, which occurs due to the dangerous shift in minerals and fluids once food is re-introduced after a long period of fasting.
It is advisable to use multivitamin supplements during extended fasting to avoid nutritional deficiencies.
Can I consume some calories when fasting?
If you find it difficult to go completely without food for 24 hours you can still achieve many of the benefits of fasting if you consume only a small number of calories during the fasting period.
This approach won’t deliver such extreme changes as fasting completely however incorporating some calories can make fasting more sustainable in the long term for many people, therefore leading to better long term results.
If you do consume calories it is important not to consume more than 800 calories in the fasting period. 800 calories should be sufficient to help avoid food cravings and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia or low blood sugar levels. The calories can be consumed as a single meal or spread throughout the day.
If you eat on fasting days, try to stick to low calorie foods which are high in fiber
How often do you need to fast?
It is only when intermittent fasting is adopted as a dietary habit over several weeks or months that a you will see real long term results, and derive benefits such as improved longevity.
If you choose the shorter fasting approach, this should be done at least 3-5 times per week. 24-hour fasts can be done 1-3 times a week. The frequency of longer fasts depends upon duration. A 48 hour fast could be done once per week but a 4 day fast should not be done more frequently than once per month.
Intermittent fasting is easier for most people to maintain than a regular diet. Start with shorter fasts and work your way up from there. Find an approach that works for you, one which you can incorporate within your routine, and stick with it. If you do you will see results.
REFERENCES
https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(17)30612-5
http://www.ncl.ac.uk/press/news/2016/02/mitochondriashowntotriggercellageing/
Cycloastragenol – a revolutionary anti-aging drug or a cancer risk?
Cycloastragenol (CAG) has been heralded by some as a miracle anti-aging agent. Early studies appear promising, showing it has the ability to increase telomere length, however there is a still a lack of quality peer-reviewed research. In addition, there is some concern that taking CAG may increase the risk of certain cancers. In this article we will discuss what CAG is, how it works and the latest findings as to its efficacy and risks.
Cycloastragenol (CAG) has been heralded by some as a miracle anti-aging agent. Early studies appear promising, showing it has the ability to increase telomere length, however there is a still a lack of quality peer-reviewed research. In addition, there is some concern that taking CAG may increase the risk of certain cancers. In this article we will discuss what CAG is, how it works and the latest findings as to its efficacy and risks.
What is Cycloastragenol?
CAG is a molecule derived from Astragalus membranaceus herb. The Astragalus herb has been used in Chinese medicine for centuries. The Chinese claimed that Astragalus can prolong life and it has been used it to treat fatigue, allergies, colds, heart disease and diabetes.
CAG is one of the active ingredients in Astragalus.
Astragalus used in Chinese medicine is one of the primary sources of CAG.
What are telomeres?
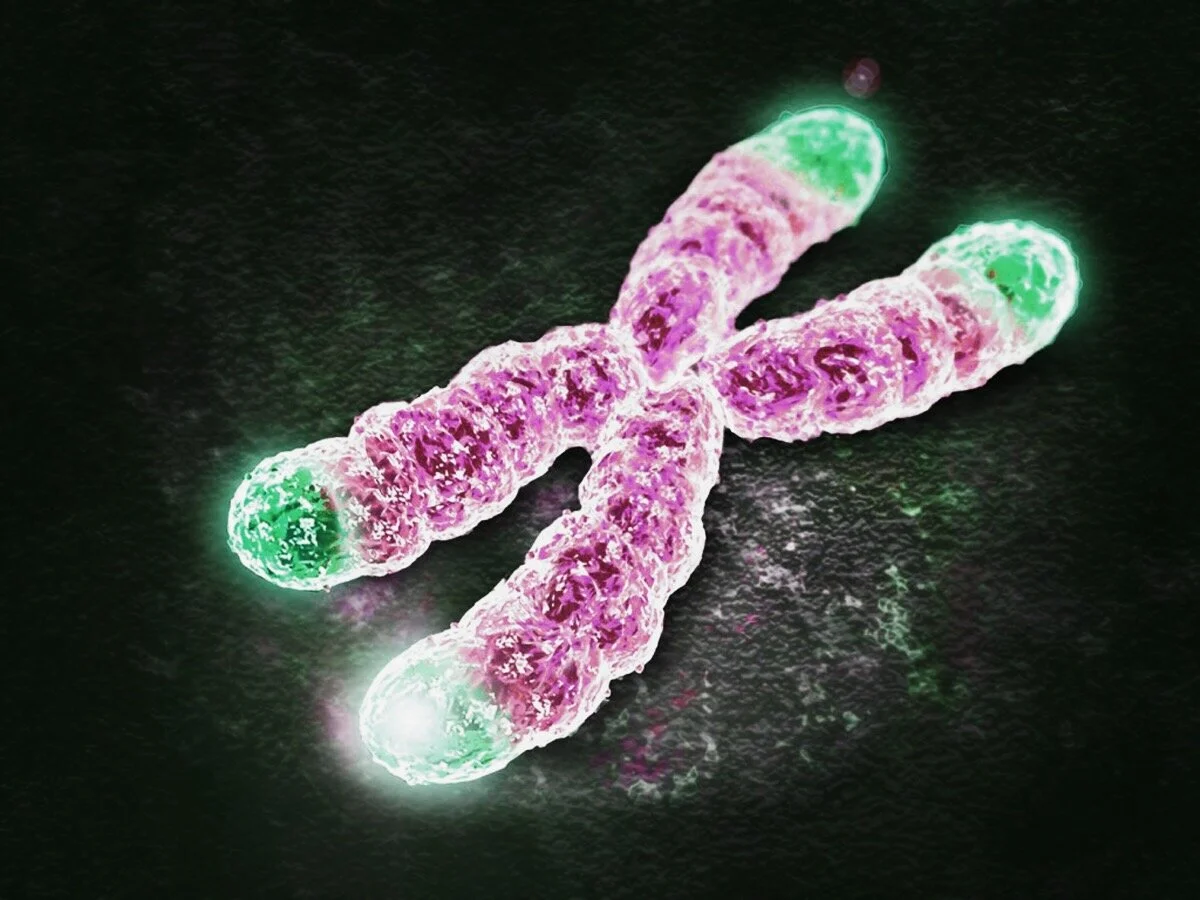
Telomeres are sequences of repeated genetic code located on the end of DNA strands.
Each time a cell divides, our DNA is copied from the old cell to the new cell. As the DNA is copied a small part of the DNA is lost from the end of the DNA strand. The telomere is the sacrificial end of the DNA strand. Each time our cells divide a part of the telomere is lost and the telomere becomes shorter.
When the telomere ends get too short, the DNA can no longer be copied and the cell refuses to divide any further. The average length of telomeres is a good indicator of biological age in most organisms (shorter = older).
Our cells divide for many reasons one of which is to replace damaged and dead cells. Our skin cells are constantly dividing as we lose approximately 30,000 to 40,000 skin cells every minute!
The number of times each cell can divide is limited. The average cell will divide between 30 to 90 times before cell death. Once this limit is reached, the cell will no longer divide, thus in theory the ability for that tissue to grow or heal would be greatly reduced, potentially leading to typical signs of aging.
Fortunately, cells have the ability to secrete an enzyme called telomerase, which can add telomeres back to the ends of the DNA. When telomerase causes telomers to become longer, it leads to the turning back of the age-clock (1).
Telomeres are the “protective caps” on the end of DNA
How does CAG work?
CAG is well absorbed by the body as it can pass through and be absorbed by the intestine. It later undergoes further metabolism in the liver.
Extensive pharmacological properties have been attributed to CAG. It activates the telomerase enzyme and consequently may causes telomere elongation, it produces anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative actions and is also reported to support healthy lipid metabolism (2).
CAG’s ability to induce telomere elongation is one of the main reasons CAG has generated so much excitement in the anti-aging community. In mice premature aging has been reversed through increased telomerase production (3).
What are the benefits of CAG?
The elongation of telomeres would allow each cell to last longer and also support the body's ability to produce new cells through more cell divisions (4). This would enable the body to replace dead and damaged cells for longer, potentially reducing aging.
Clinical research studies have demonstrated that CAG can activate telomerase in humans (5). These properties of CAG led to the belief that CAG could be used as an antiaging agent.
Later research studies were focused primarily on assessing whether CAG could actually defy the signs of aging. In various studies CAG has been shown to reduce fine lines and wrinkles, boost immunity and improve vision (6), (7), (8).
While these studies demonstrate CAG may be beneficial in increasing healthspan, no studies have yet conclusively demonstrated CAG’s ability to extend lifespan in humans.
Is CAG safe?
There is some concern that CAG may increase the risk of cancer. Critically short telomeres lead to apoptosis (cell death), in the case of cancer this would be a good thing! By preventing shortening of telomeres, the bodies ability to induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is affected. Apoptosis is the body’s natural defense mechanism that can help to kill the abnormal cancer cells selectively (9).
In fact, telomeres are already elongated by telomerase enzyme in nearly 80% of tumors, that is one of the reasons they are so hard to kill (10). Elongation of telomeres due to telomerase could in theory prevent the destruction of cancer cells thereby contributing to tumor growth.
Apoptosis, is the death of cells which is a normal and natural part of development
A lawsuit has been filed by an employee against the manufactures of a well-known CAG product.
The employee, Egan, was hired by Patton in May 2011 to help expand the reach of Telomerase Activation Sciences in foreign markets. Telomerase Activation Sciences sells a supplement called TA-65, which is claimed to elongate short telomeres.
Egan was asked to take these pills twice a day. However, later, on 14 September, he was diagnosed with prostate cancer, which, according to the lawsuit filed by Egan, could be due to TA-65.
However, research studies have not been able to establish any cancer risk associated with the use of CAG. Laboratory research studies in animals have shown that CAG does not induce any genotoxic or toxic effect. In a research study, the administration of CAG to rats for 3 months did not show any rise in the incidence of cancer (11).
This indicates that while physiological processes involved in cell division do suggest that CAG could cause cancer, there has been no clinical evidence to prove this claim.
Conclusion
CAG looks like a promising anti-aging compound. While it has not been proven to increase lifespan yet it has been shown to reduce various age associated biomarkers. In addition it has been shown to reduce the signs of aging such as fine lines and wrinkles. It may also reduce the risk of degenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, Parkinson’s, retinopathies, and cataracts.
However, it is advisable to not ignore the potential risk of cancer. Careful evaluation of the safety of CAG through further long-term scientific studies is required. Anyone with a personal or family history of cancer may be advised to avoid CAG until more long-term safety studies have been conducted.
References:
What causes a hangover and what can we do about it?
The primary causes of a hangover are dehydration, oxidative stress, inflammation and nutrient deficiencies. In this post we outline what you can do to protect against each of these - to minimize your hangover.
What causes a hangover?
The primary causes of a hangover are believed to be dehydration, oxidative stress, inflammation and nutrient deficiencies.
Dehydration
Alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it causes you to excrete more fluids (pee more) than you drink. This is caused by alcohols effects on the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is responsible for producing vasopressin. Vasopressin is the hormone which tells your kidneys to reabsorb water rather than flushing it out. As alcohol slows down the functioning of the pituitary gland, the production of vasopressin is greatly reduced, thereby signaling the body to pass most of the fluids it receives straight through.
Feeling parched?
Oxidative Stress
Most of the alcohol you consume is chemically broken down in the liver. Enzymes break the alcohol down into acetaldehyde and then again into acetic acid. Acetic acid is subsequently converted into either fatty acids or carbon dioxide and water. Several studies have shown a correlation between the level of acetaldehyde and hangover severity(1). As the level of acetaldehyde rises the level of glutathione declines. Glutathione is our bodies primary antioxidant. Antioxidants help fight oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is damage caused by excess oxygen in the body. Lower levels of glutathione means more oxidative stress causing damage to our cells.
Inflammation
Several studies have also demonstrated that an imbalance in the immune system could be a contributor to hangover symptoms. This is caused by alcohol inhibiting the metabolism of certain inflammatory cytokines. Cytokines are proteins which play a crucial role in cellular communication and activation. Cytokines can either be pro-inflammatory (causing inflammation) or anti-inflammatory (reducing inflammation). As alcohol increases the level of inflammatory cytokines this can lead to increased inflammation which can cause symptoms such as nausea, headache and fatigue(2).
Nutrient and vitamin deficiencies
Excess alcohol consumption can lead to various nutrient deficiencies. In particular alcohol can exhaust the bodies supply or choline. Choline is an essential nutrient and is critical for the structural integrity of our cells. Choline is also used to produce acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter important for memory, mood and muscle control. Drinking can also deplete the bodies supply or several vitamins and minerals such as vitamin A, C, D, E, K and B.
All of these factors combined contribute to that hungover feeling.
what can we do to prevent a hangover?
Avoid sugary drinks and dark liquors
Sugar also has a dehydrating effect on the body. When the body senses it has excess sugar it causes you to urinate more, similar to alcohol. In addition, the liver plays an important part in processing both alcohol and sugar. Adding sugar to your alcoholic beverage therefore increases stress on the liver.
Many alcoholic beverages contain congeners, these are found in larger amounts in dark liquors. They can be toxic to the body and cause further oxidative stress. Excess consumption of congeners can increase the severity of a hangover(3).
Drink water and electrolytes for hydration
There is no easy way to avoid dehydration completely but a couple of simple things can minimize the extent of dehydration, these include:
- Ensuring you are well hydrated before you begin drinking
- Drinking one glass of water between every alcoholic beverage
- Consuming one liter of water at the end of the night before going to bed
Taking electrolyte supplements can also be helpful, but avoid any which contain lots of sugar. Simply adding some salt to your water helps, or try drinking a glass of vegetable/chicken broth/bullion before bed.
Top up on antioxidants
Supplementing with phenolic compounds such as resveratrol, pterostilbene or astaxanthin may improve alcohol metabolism and offset the increase in oxidative stress caused by alcohol consumption. One study showed supplementing with sprouted peanut extract in rats, which is high in resveratrol reduced symptoms of hangovers(4). Another study in humans showed that supplementation with antioxidants while drinking reduced plasma alcohol concentrations and oxidative stress(5).
Supplementation with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and Vitamin C may also help. NAC is a precursor to glutathione, an antioxidant that helps metabolize alcohol. Glutathione is also the main scavenger of free radicals in our bodies. Vitamin C assists in the conversion of NAC to glutathione. NAC is used in hospitals to treat alcohol poisoning. Glutathione is poorly absorbed by the body when taken orally, therefore NAC is the better option for supplementation.
If you don’t want to take supplements try to eat some foods rich in antioxidants before you go out drinking. Some examples include berries, turmeric, pecans, artichokes and kale.
Take anti-inflammatories (or curcumin!)
Anti-inflammatories such as aspirin or ibuprofen reduce the level of inflammatory cytokines and have been shown to alleviate hangover symptoms(6). These medications should only be taken with food as they can aggravate an already sensitive stomach after a heavy night drinking. A natural alternative is curcumin. Curcumin is a powerful anti-inflammatory and is gentler on the stomach. Try supplementing with curcumin before drinking, before bed and in the morning.
Take vitamins and choline
Topping up your vitamin stores with a multivitamin before bed can help replenish what a big night of drinking has taken out. As alcohol depletes your bodies choline stores it is also a good idea to eat foods rich in choline such as salmon, eggs, liver or peanuts. Alternatively, you can take a choline supplement.
Salmon and eggs are a rich source of choline.
Exercise
Some light cardio the morning after a night of drinking will get your endorphins pumping and should make you feel better. It also helps to sweat out some of the toxins left over from drinking. Just remember to drink plenty of fluids as you are likely dehydrated after a big night out. It also doesn’t need to be a marathon, just don’t lie in bed all day!
Our top supplement picks
NAC, curcumin, choline, astaxanthin and plenty of water!
References
Everything You Need to Know About Heart Rate Variability
Heart Rate Variability – or simply HRV – is said to be an indicator which can be used to monitor overall health, biological age, aerobic fitness and levels of stress. HRV has recently become a popular metric among biohackers and fitness fanatics, especially as technological advances now make it possible to measure at home.
What is Heart Rate Variability?
Heart Rate Variability – or simply HRV – is said to be an indicator which can be used to monitor overall health, biological age, aerobic fitness and levels of stress. HRV has recently become a popular metric among biohackers and fitness fanatics, especially as technological advances now make it possible to measure at home.
HRV is the difference in timing between each heartbeat interval. The variation between heartbeats is controlled by a particular part of the nervous system referred to as the Autonomic Nervous System or ANS.
What is the ANS?
The ANS controls most of our internal organ functions, such as the heart, stomach and intestines. The ANS works whether we want it to or not, that is why you don’t have to consciously decide for your stomach to digest your food.
The ANS is a critical part of our breathing, blood pressure and digestion processes. The ANS helps keep the bodies internal environment (temperature, blood sugar, oxygen etc.) in balance.
The ANS is divided into two sub-components, namely the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system. In layman’s terms, these are known as the relaxation response and the fight-or-flight reaction (1).
The parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic system, or relaxation response, helps with the day to day tasks such as digestion, slowing the heart rate and decreasing blood pressure.
The sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic system, or fight and flight response, prepares the body for energy output and protects it from injury. It shuts down the gut, speeds up heart rate, increases blood pressure and increases blood sugar for energy consumption.
The sympathetic system is associated with the fight or flight response.
The brain responds to stimuli in our environment and subconsciously decides whether the body should be relaxed or in a fight or flight state. The brain sends signals from the hypothalamus to the ANS to trigger these responses in the rest of the body.
A poor night’s sleep, a stressful day at work or an argument with a loved one are some examples of negative stimuli which can trigger the fight or flight response. The body is usually capable of handling negative stimuli on a day to day basis. However, if one constantly experiences too much stress and unhealthy relationships with others, this may result in an excessive fight-or-flight response.
What Does Your Heart Rate Variability Tell You?
For a regular healthy person, the heart rate variability should increase whenever they engage in relaxing activities. If that person is doing yoga, lying in bed or simply resting, their parasympathetic nervous system is in control and their HRV is high. On the contrary when stressed, the sympathetic nervous system takes control, this results in a lower HRV (2).
HRV levels naturally change in response to your day-to-day encounters and interactions. However, chronic stress can result in the sympathetic nervous system or fight or flight response being in constant control. In healthy individuals the heart is able to quickly switch between sympathetic and parasympathetic states, resulting in a high HRV, whereas people with cardiac problems, or experiencing chronic stress may show a low HRV.
Research has shown a relationship between low HRV and depression, anxiety, cardiovascular disease and an increased risk of death (3).
A low HRV could predict an early death!
How can I use HRV?
Stress tracking
Measuring HRV over a few minutes at the same time each day (e.g. upon waking) can provide you with a useful metric for monitoring stress levels. Knowing when your HRV is low can help you incorporate healthy habits into your day when they are most needed.
Activities such as mindfulness, meditation, sleep, and physical activity can all help increase HRV.
Prevent over-training
Elite athletes and trainers monitor heart rate in conjunction with HRV to conduct various tests to determine when the body is in need of rest or conversely when it is recovered and ready to train again. Conducting such tests reduces the risk of overtraining.
Many of the HRV monitoring devices and apps have such tests built in. One example is the Orthostatic Test from Polar (4).
What is a good score?
Generally a higher HRV score is an indicator of good health however it is not easy to define what constitutes a “good” score. HRV scores will change significantly for individuals depending on time of day, their position when the reading was taken and their activity levels. There are also a number of different ways to measure HRV and as yet there is no standardized approach (5).
It is therefore important to only compare HRV scores taken at similar times under similar circumstances and on the same device. For example upon waking, in a seated position and using a polar chest strap with the Welltory app.
The best way to judge your HRV is to monitor it over time. It is worth taking note of the average score when you are in periods of low stress, such as a holiday, and then comparing the readings on days after intense exercise or when you are experiencing lots of stress at work. There are a number of apps (mentioned below) which allow you to easily monitor this.
For those determined to know how they stack up against the general population we have included some stats below. These values are based upon the rMSSD method (6,7,8,9):
Young, highly trained individuals 70 - 120
Young sedentary individuals 30 - 50
In patients with chronic heart failure in the 20s
Methods of measuring Heart Rate Variability
Most devices employ one of two approaches to monitor HRV, an ECG or PPG.
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is the most accurate way to detect HRV. An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart. This method requires electrodes to be placed directly on the chest. The electrodes require secure contact with the skin to work effectively.
PPG
Photoplethysmography (PPG) differs from an ECG in that instead of measuring the electrical activity it illuminates the skin with a small light and then measures changes in light absorption. The skins light absorption changes in response to blood pressure and blood flow, thus this can be used to monitor HRV.
While PPG can produce good results it can easily be disrupted, any motion during measurement or light pollution can result in an incorrect reading.
Recommended devices for HRV monitoring
Gone are the days when you have to be sent to the hospital just to get your HRV checked. There are now many compact and convenient devices which allow you to check you HRV whenever you want.
A chest strap which utilizes ECG technology will provide the most accurate results. Some fitness watches also claim to produce reliable HRV measures but results vary, most of these watches use PPG technology.
Recently a number of mobile phone apps have been released allowing users to measure HRV using their phone. The apps access the phones camera which uses PPG technology to measure HRV. Some companies claim these measures are accurate however there is still a lack of independent studies. When we tested these apps using both PPG via the camera and ECG using a chest strap we found the results varied significantly.
For the average user curious about HRV and interested in taking the occasional HRV reading we recommend downloading one of the apps below and using your phones camera to take a PPV reading. For the more serious enthusiast interested in monitoring HRV on a daily basis or during your exercise workout, we suggest investing in a chest strap.
Recommended mobile apps
Here are just some of the best apps when it comes to measuring and recording HRV.
Welltory
This is one of the most user-friendly HRV-measuring apps for both iPhone and Android users.
Welltory allows users to measure their HRV using the phones camera, the camera uses PPG technology to measure HRV. Welltory can also be used with a variety of chest straps and fitness watches for a more accurate measure of HRV.
Welltory also connects to a very wide range of other fitness trackers and apps. Welltory has a user friendly interface and can break down your HRV results easily and divide them into comprehensible categories. These categories include performance, energy and stress levels.
The basic version is available free however a fee is required to access to access premium features.
HRV4Training
HRV4Training is another app that you can download whether you’re on an iPhone or Android device. This app also allows you to use your phones camera to obtain a PPG reading of your HRV. For a more accurate reading the app can also be used with a chest strap to obtain an ECG reading.
It’s designed to track your metrics in 30-days and then provide training suggestions on how you can do better. Unfortunately there is no free version and the basic version starts at $9.99.
Elite HRV
Elite HRV is another free app available to both Android and iPhone devices. The main drawback is that it requires an external heart rate monitor, it will not allow you to use your phones camera to generate a PPV reading. We also found the design is not as user friendly as Welltory or HRV4Training.
The app is free for both operating systems, but to access the full feature set you need to pay $4.99.
Recommended devices
The apps Welltory and HRV4Training will allow you to take a PPG HRV reading using your phones camera. A PPG HRV reading can also be obtained using most high end fitness watches (Garmin, Polar) and even the Apple watch. For the average person a PPG reading is sufficient.
For the serious enthusiast who wants a more accurate ECG reading a chest strap is required. Below are some suggestions.
Polar H7 Bluetooth Heart Rate Sensor
Polar is an established company, well-known for its heart rate and exercise-assistive products. Their H7 Bluetooth Heart Rate Sensor can be comfortably worn on the chest and is available in two sizes. It has up to 200 hours of battery life.
The H7 uses ECG technology for a more accurate reading and is one of the more affordable HRV monitoring devices available.
Polar H10 Bluetooth Heart Rate Sensor
This is the newer model from Polar, some of the upgrades include a doubling of the battery life to 400 hours. And this model is waterproof,
so suitable for swimmers.
Garmin Premium Heart Rate Monitor
This heart rate monitoring device from Garmin measures your HRV while keeping you comfortable with its soft strap. It’s also a waterproof device so you can use it while swimming.
It can easily transmit data to any other Garmin fitness tracker or your preferred iOS or Android app.
What is High-Intensity Interval Training and does it work?
If you ask people why they are not able to exercise, many will tell you that it is because they do not have the time. This is precisely why High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is interesting. Proponents of HIIT claim that it increases fat burning and cardiovascular performance - more than traditional forms of exercise and it requires significantly less training time.
If you ask people why they are not able to exercise, many will tell you that it is because they do not have the time. This is precisely why High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is interesting.
Proponents of HIIT claim that it increases fat burning and cardiovascular performance - more than traditional forms of exercise and it requires significantly less training time.
What is HIIT?
HIIT requires a person to exert maximum effort through quick, extreme bursts of exercise, followed by subsequent short recovery periods, this is then repeated several times.
The intention is to get your heart rate close to its maximum and then allow it a period of recovery before repeating. Typically, a HIIT workout lasts only 15-30 minutes.
When performing a HIIT workout you need to ensure the sets are intense enough to get your heart rate to around 80% of its maximum.
You can use the formula below to calculate the optimal HIIT heart rate for your age.
( 208 - ( age x 0.7 ) ) x 80 percent = 80% of max heart rate
What are some examples?
Walk and Sprint or Jog and SprinT
A common approach is to do a 1 minute walk followed by a 30 second sprint, repeated several times. As you progress, you can swap the walking with a light jog, also the number of repetitions can be increased. Running sets of stairs can achieve a similar effect.
Sprint cycling
Another approach is to perform a series of 30 second sprints on a stationary exercise bike, with a minute of rest in between each sprint.
Start with 5 or so repetitions and work your way up from there.
Rowing ergometer
An excellent way to get your heart rate up quickly is on the rowing machine.
Again, a series of short 30 second sprints with a 1 minute recovery period should achieve good results.
Bodyweight reps
The bodyweight rep approach involves choosing a bodyweight exercise (e.g. pushups, squats, sit ups, lunges) and doing short sets of 10 -15 reps. Between each set allow yourself a 30 second recovery period.
You can start with a few sets and increase it over time. For best results try alternating between several exercises.
Sports & Martial arts
Although sports and martial arts aren’t normally considered interval training, certain sports can have a similar effect.
Doing intense rounds of pad work in boxing, rounds of high intensity sparring in Muay Thai, or rolling at full tilt in Jiu Jitsu can get your heart rate close to its max.
Between rounds your body has time to recover, and this is then repeated several times.
Does HIIT work?
For weight loss
In short, yes.
Studies have shown that individuals can burn more calories performing a HIIT session than spending the same amount of time performing a steady state exercise (1).
In addition, after a HIIT workout the metabolic rate remains higher for several hours after exercise. This means your body continues to burn calories at a higher rate, even after the workout. While this effect also occurs with regular exercise it is more pronounced with HIIT training (2).
Combined these effects mean HIIT can be a very effective tool for weight loss. Even with only a relatively low amount of time investment HIIT has been shown to work well. (3).
For cardiovascular fitness
Research indicates HIIT can reduce resting heart rate and blood pressure in overweight individuals with high blood pressure (4).
One study showed that HIIT may be more effective at lowering blood pressure than moderate-intensity exercise, which is usually what the doctor recommends. (5).
Another study showed that HIIT significantly enhanced cardiovascular performance (VO2max and O2 pulse and power output) in active men and women. (6)
For muscle mass
Some HIIT workouts are likely to lead to increases in muscle mass in the muscles utilized in the workout. However HIIT training itself is not the ideal tool for muscle gains, weight training is still the most effective way to pack on muscle.
If you are looking to gain muscle with your HIIT workout then it is best to use a HIIT workout which incorporates weights, circuit training such as CrossFit is a good example.
Other health benefits
Anti ageing
HIIT helps to offset age-related decline in muscle cell function.
One study found that muscle cell function, especially cell metabolism improved after only 12 weeks of HIIT training. HIIT also improved age-related decline in mitochondria, which means that it helped in promoting healthy cell growth, which combats overall physical deterioration (7).
Reducing blood sugar and insulin resistancE
HIIT has been found to be potentially beneficial to people at risk of type 2 Diabetes. It has been shown to be more effective than traditional exercise for reducing blood sugar and increasing insulin resistance (8).
What are the risks?
Cardiac risk appears low
Some critics of HIIT have expressed concern that pushing the heart close to its maximum may increase the risk of a negative cardiac event. The research indicates this is not the case.
Ulrik Wisløff, head of the Cardiac Exercise Research Group at the Norwegian School of Science and Technology concluded that risk of a cardiovascular event is low for people with heart disease that perform HIIT (9).
Wisloff and his colleagues have analyzed approximately 50,000 hours of HIIT data, which they collected from patients with heart disease in Norway. Only two instances of cardiac arrest, both of which were non-fatal, were recorded in seven years of data.
Wisloff states that it’s generally much more dangerous for people with heart disease not to perform HIIT than to perform it.
Despite these finding anyone with unstable angina or severe heart issues should speak with their doctor before performing HIIT.
Higher risk of injuries to muscles, ligaments and joints
The biggest risk factor from HIIT is injury. A study conducted by Rutgers New Jersey Medical School showed that HIIT significantly increases the risk for injury (10).
The research team analyzed records in the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System from 2007 through 2016, and they found 3,988,902 injuries caused by exercise equipment such as barbells, kettlebells, and boxes, or calisthenics such as burpees, push-ups, and lunges -- all of which are common in HIIT programs. Most of the injuries involved knees, ankles, and shoulders.
Conclusion
HIIT is a powerful tool for weight loss, improving cardiovascular health, lowering blood sugar and fighting the effects of age. It can be a great way to achieve good results for people who have limited time to work out.
While there is some risk of injury, the improvements in overall health should lower the risk of many other more life-threatening diseases.
To reduce the risk of injury it is important to understand if you have any pre-existing conditions or physical weaknesses. Tailor your workout around any such weaknesses and make sure you have proper instruction on technique. Before each work out warm up appropriately, and ensure adequate recovery time between sessions.
REFERENCES:
Foods that you can eat on a Ketogenic diet
One of the most difficult aspects of a keto diet is knowing what you can and can’t eat. In this article we will outline some keto friendly foods. Some people see the keto diet as an excuse to eat meat and cheese all day long, but this is neither healthy nor sustainable. It is important to keep eating vegetables to ensure you are getting the vitamins, nutrients and fiber you need. Also it is possible for Vegans to follow the keto diet!
One of the most difficult aspects of a keto diet is knowing what you can and can’t eat. In this article we will outline some keto friendly foods.
Is it all meat and dairy?
Some people see the keto diet as an excuse to eat meat and cheese all day long, but this is neither healthy nor sustainable.
It is important to keep eating vegetables to ensure you are getting the vitamins, nutrients and fiber you need.
Many vegans assume a keto diet needs to be high in meat and dairy, and therefore a keto diet is not for them, this is not true, there are many vegan friendly keto options.
What does net carbs mean? Does fiber count?
If you’re going to start the keto diet, first you need to get the carbs out of your kitchen and replace them with some keto friendly options. But before you throw everything away it is important to first understand the difference between total carbs and net carbs.
While fiber is a type of carbohydrate it isn’t absorbed the same way as normal carbs, therefore it is okay to eat while on a keto diet. Fiber makes you feel full and keeps you regular. Many people report they experience constipation while on a keto diet, this is often because they aren’t consuming adequate levels of fiber. If counting carbs on a keto diet you should count “net carbs”, net carbs is total carbs less fiber.
Below is a list of some low “net carb”, keto friendly foods which you can safely eat to your hearts content.
okay so what can I eat?
Seafood
Seafood is a great source of Omega-3 fatty oils, vitamins and minerals. It is high in protein and low in carbs.
If you are pregnant or concerned about mercury, some fish which are lower in mercury include salmon, tilapia, shrimp, tuna, cod and catfish.
Non-starchy vegetables
Vegetables are a great source of fiber, antioxidants and essential nutrients.
However some starchy vegetables are high in carbs and should therefore be avoided (e.g., potatoes and squash).
Some low carb options include: Bell peppers (capsicum), kale, broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, mushrooms, zucchini, spinach, lettuce, cucumbers,
brussel sprouts, celery, tomatoes, radishes,
onions, eggplant and cabbage.
Cheese
One of the great things about the keto diet is you can almost eat as much cheese as you want!
Hard cheeses are especially low in carbs, but soft cheeses are fine to eat too.
Cream
That’s right, real full fat cream is also fine to consume on a keto diet!
Just make sure it isn’t sweetened as some of the store-bought whipped creams are sweetened with sugar.
Dark Chocolate
A bit of dark chocolate is generally okay, but read the label as it can differ greatly.
Generally, the very high cocoa content (95% and 99%) chocolates have the least carbs.
Avocados
A whole average avocado weighs around 200 grams and contains 18 grams of carbs. However approximately 14 of these 18 grams are fiber, leaving only 4 grams of net carbs!
Meat
Meat and poultry are great sources of protein, vitamins and minerals.
It is best to eat grass fed meat which is higher in important vitamins and antioxidants than grain fed meat.
Eggs
Eggs are a great source of protein and vitamins.
Most of the nutrients are contained in the yolk of the egg, therefore it is important to eat the whole egg, not just the white.
Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are high fat, low carb foods which are also high in fiber.
Particularly low in net carbs are Brazil nuts, Macadamias, Pecans, Walnuts, Chia seeds and flaxseeds.
Butter and oils
Butter is fine to eat on a keto diet, but best to avoid margarine which often contains preservatives and chemicals.
Olive oil and coconut oil are both excellent sources of fat while on a ketogenic diet.
Berries
Berries are high in fiber and low in net carbs, so unlike most fruit they are okay to consume on a keto diet. They are also a great source of antioxidants.
What is the ketogenic diet, does it work, how does it work, and is it safe?
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a low carb, high fat diet which is the new health food craze, but is it safe? And does it work? We examine some of the most recent scientific research to find out.
What is it?
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a low carb, high fat diet. Consuming low levels of carbohydrates forces the body to burn fats as the primary fuel source, this is known as ketosis. People following the keto diet usually try to limit carbohydrates to no more than 5% of their calories, fats account for up to 75% of their caloric intake and proteins approximately 20%.
Does it work?
For losing weight? In short, yes.
There are over 20 double-blind, placebo controlled studies showing that the keto diet, or at least a low carb diet is more effective than high carb, low fat diets for losing weight (1).
In addition, ketogenic diets lead to large reductions in blood sugar and insulin levels, this is believed to reduce inflammation and lead to a range of other health benefits including
Increased ATP and cellular energy (2)
Lowering risk of heart disease (3)
Protecting brain function (4)
Inhibiting growth in certain types of cancer (5) (6) (7)
Reducing seizures in epileptic children (8)
How does it work?
The body uses two sources of fuel to produce cellular energy, carbohydrates and fats. When we are consuming high levels of carbohydrates the body prefers this as a fuel source, and much of the fat we consume is stored for later use. However when the body does not have enough carbohydrate to burn the liver starts breaking down fats, via ketosis. This process converts the fat into ketones, which can then be consumed by the body as an energy source.
Leptin induced satiety
One of the main reasons people lose weight while on the keto diet is due to leptin induced satiety, that means you feel full after consuming fewer calories.
Leptin is a hormone produced in fat cells, which is responsible for telling your brain when the body has sufficient fat stores. High levels of leptin give the brain the signal that is has enough fat and can resume normal metabolic function. Low levels tell the body that it needs to conserve fat, thereby leading to hunger, reduced motivation to exercise and ultimately weight gain. By consuming more fats, you send more leptin to the brain, signaling that you are full, so you don’t feel as hungry (9) (10) (11) (12).
People with obesity have high levels of leptin but often have leptin resistance, therefore their brain does not respond to the increased levels of leptin (13). The consumption of a diet high in sugar seems to lead to leptin resistance (14). It has been suggested that the Keto diet can reset the leptin sensitivity in such people, while this may be possible there is not yet sufficient evidence to support the claim that the keto diet can reset leptin sensitivity.
Reduced food cravings
A second mechanism by which keto works is via insulin and dopamine. Dopamine is often referred to as the motivation hormone, the brain usually produces dopamine in response to a positive surprise however drugs such as cocaine also cause releases of dopamine. When consuming a high carb diet spiking blood sugar levels cause releases of dopamine. The consumption of carbohydrates also causes the level of insulin in the body to spike, insulin has been shown to amplify the effect of dopamine (15). Therefore leading to powerful food cravings. The keto dies reduces levels of insulin thereby reducing these dopamine induced food cravings.
Some studies have shown that even when total caloric consumption is equal, those following the low carb diet tend to lose more weight. However this could be due to the fact that lower muscle glycogen stores results in lower water retention (16) (17) (18).
Is it safe?
It has a positive impact on cholesterol
One of the main concerns about the ketogenic diet is its potential impact on cholesterol. However most of the evidence suggests the Keto diet has a positive impact on cholesterol. Firstly the keto diet tends not to raise LDL cholesterol and it appears to raise the level of “good cholesterol”, or HDL cholesterol. Higher HDL cholesterol levels are associated with lower risk of heart disease (19) (20) (21).
It reduces blood sugar
The keto diet may also be beneficial for diabetics. One study in type 2 diabetics found that the low carb diet drastically reduced blood sugar levels, and 90% of the participants were able to actually reduce their need for their diabetes medications (22).
While the keto dies has been shown in some studies to be beneficial for diabetes, anyone suffering from type 1 or type 2 diabetes should consult a doctor before starting a keto diet. For people with diabetes, ketosis can trigger a dangerous condition called ketoacidosis. This occurs when the body stores up too many ketones and the blood becomes too acidic, this can cause damage to the liver, kidneys and brain, in extreme cases it can be fatal.
Excess ketones can place a strain on the kidney and liver
As ketones are acidic excess production can place strain on the kidney and liver. For healthy people following a ketogenic diet the levels are not a concern however anyone with kidney or liver issues should consult a doctor before deciding to follow a keto diet.
Lastly the keto diet is not an excuse to eat bacon all day. A healthy Ketogenic diet includes lots of vegetables and lean sources of animal proteins. Make sure you follow a diet which is varied, and you are getting plenty of vitamins and minerals. Lastly as with all diets we suggest cycling on an off for periods throughout the year.
The next article in this series provides more information on what foods you can eat on a ketogenic diet.
References
1. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/23-studies-on-low-carb-and-low- fat-
diets#section1
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14769489
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22905670
4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2367001/
5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1819381/
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25666556
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17313687
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11581442
9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9771856
10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2430504/
11. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3602984/
12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3244537/
13. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0026049514002418
14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2584858/
15. https://neurosciencenews.com/insulin-dopamine-levels-2934/
16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC538279/
17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17823420
18. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11745-008-3274-2
19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15505128
20. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11745-008-3274-2
Hacking aging - Part 2
This is the second part of the series on anti-ageing. In this article we will examine some promising approaches to hacking ageing, backed by scientific research, including fasting and various supplements.
This is the second part of the series on anti-aging. In this article we will examine some promising approaches to hacking aging, backed by scientific research, including fasting and various supplements.
Fasting
What is fasting and does it work?
Fasting is going without food, or consuming a calorie restricted diet for an extended period of time, some fasts are as short as 16 hours, some can be months long.
Fasting is probably one of the most extensively researched and evidence backed approaches for longevity. Strong evidence exists that restricting calories increases lifespan in mice and humans.
Fasting need not be constant, instead fasting for periods of time at regular intervals is sufficient to generate the same benefits seen in long term fasting studies. Interestingly rather than going without food completely similar results to fasting were observed using a Fasting Mimicking Diet (FMD), that is a diet low in calories, sugars, and proteins but high in unsaturated fats (1), one such popular diet is the Keto diet.
How does it work?
When fasting the body no longer has enough carbohydrates to sustain it and therefore switches to autophagy for its energy source. Autophagy literally translated from greek means “to eat oneself”.
The body feeds on the various damaged parts of cells such as cell membranes and proteins, thereby removing them from the body. When these sub-cellular parts are removed they are replaced with new parts, thereby restoring the cells to proper function.
In addition to promoting autophagy fasting also promotes the production of growth hormone, which helps the body produce these new replacement parts (2).
What are the benefits?
One study compared people who consumed a fasting mimicking diet for 5 days once a month for 3 months to those following a regular diet. Those who followed the periodic fasting diet showed reduced body weight and fat, lower blood pressure, and decreased IGF-1 hormone. IGF-1 has been linked to aging and disease. Further studies showed the fasting diet also decreased cholesterol and markers for inflammation (3). Animal studies have demonstrated a range of benefits including wound healing (4), and brain function (5).
How can I implement fasting in my daily life?
There are a number of ways to fast, some common approaches include:
16:8 fast: This involves limiting consumption to an 8 hour window per day. This cycle can be practiced as often as you like, once, twice per week or every day. An example of this would be skipping breakfast, but having a healthy lunch and dinner.
24 hour fast: This involves skipping meals for 24 hours, e.g. if your last meal is dinner you do not eat again until dinner the following night. This type of fast is more difficult and therefore not practiced as often, some people choose to do this once a week or once a month.
5:2 fast: This involves eating regularly for 5 days a week and eating a calorie restricted diet (no more than 500 calories per day) for 2 days a week.
Similar results can be achieved by following a calorie restricted diet such as the Keto diet. More information on the Keto diet can be found here.
Calorie Restriction Mimetics (CRM)
Let’s face it, fasting sucks, it is difficult for most people to maintain a fasted state, or even maintain intermittent fasting over a long period, therefore scientists have been researching Calorie Restriction Mimetics (CRM’s).
CRM’s are compounds when ingested mimic the body’s response to being in a fasted state. One promising group of CRM’s are sirtuin activators.
What sirtuans and sirtuan activators?
Sirtuans are proteins in the body which are responsible for DNA maintenance and repair. These genes are activated when the body senses it is in a stressed state (e.g. fasting). One of the seven sirtuans found in humans, SIRT1, can be activated by natural compounds known as polyphenols. Polyphenols are found in plants, where they are involved in defending plants from ultraviolet radiation and pathogens. Polyphenols include pterostilbene which is found in blueberries, resveratrol which is found in the skin of grapes and curcumin.
What else is required for sirtuan activators to work?
Sirtuans can only function in the presence of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), NAD+ is a coenzyme found in all cells, it is responsible for helping turn nutrients into energy and regulating other biological activity. NAD+ levels in humans decline with age. Therefore boosting levels of NAD+ can help Sirtuans to continue functioning into old age.
Do these supplements work and can they by purchased?
Recent studies have highlighted potential positive effects from increased NAD+. One study showed that mice supplemented with NAD+ precursers showed increased levels of DNA repair and the tissues of 2 year old mice appeared identical to that of 3 month old mice (6). Another study showed increased levels of cognitive ability (7). There are not yet any results from human trials.
NAD+ can be taken directly or NAD+ levels can be increased by supplementation with the NAD+ precursors Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) or Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN), both have been shown to raise the levels of NAD+ in the body. NR and NMN are derived from nicacin which is a form of vitamin B3, an essential human nutrient.
Most of these supplements can be purchased online, but beware are a lot of inferior products, and many which are not what the claim to be. Make sure you go with a reputable brand.
Senolytics
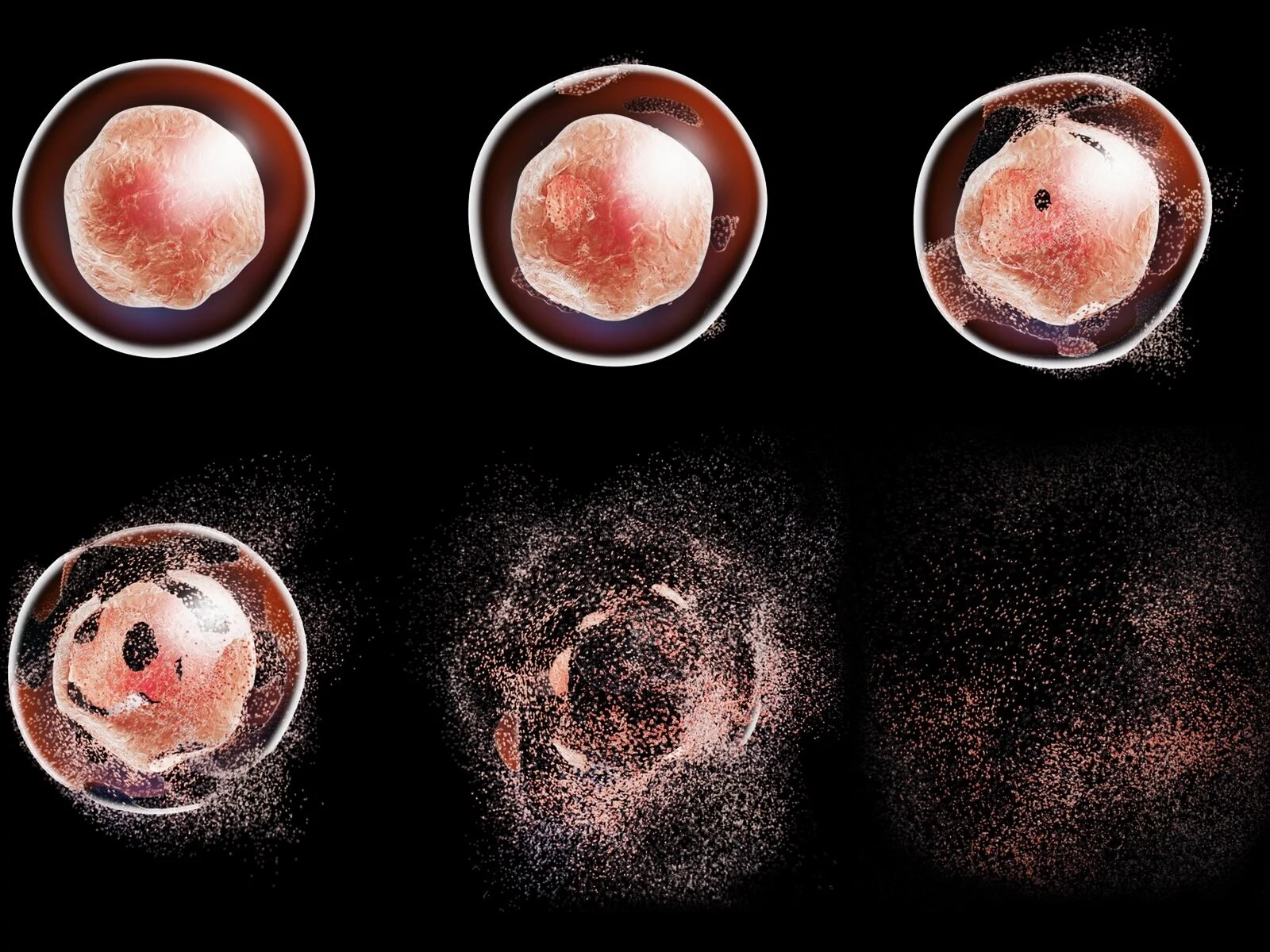
What are senescent cells?
As we age the body accumulates an increasing number of senescent cells. Sensescent cells are cells which are not functioning properly, but have not yet died off and been recycled, as cells are when we are younger.
Senescent cells secrete inflammatory factors, and appear to play a role an important role in ageing and many age related diseases including dementia, diabetes and cardiovascular disease (8).
Do senolytics work, and where can I purchase them?
The class of drugs known as senolytics target senescent cells, removing them but leaving healthy cells untouched. In various mice studies it has been shown that removal of senescent cells can prevent or delay tissue dysfunction and extend healthy lifespan (9, 10).
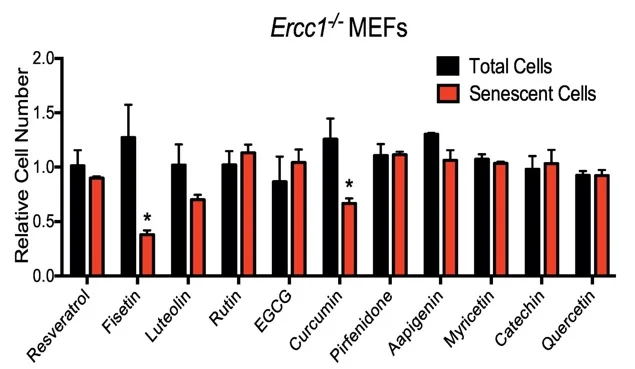
Many plant based compounds have powerful senolytic effects, one study compared the senolytic efficacy of various plant compounds in mouse cells and in senescent human fibroblasts, the results can be seen in the chart below (11).
Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were treated with a panel of flavonoid compounds, and the the viability of senescent cells and total cells were measured.
Among the 10 flavonoids tested Fisetin was the most effective. Fisetin is a natural compound found in strawberries, apples, cucumbers, grapes and onions. There are only a very few suppliers online, more common is curcumin, which can easily be purchased, fresh or in pill form. The bioavailabiliy of pure curcumin is relatively low, however taking it with piperine has been shown to increase its bioavailablity by as much as 2000%.
Metformin
No longevity discussion would be complete without mentioning Metformin. Metformin is a drug used to treat diabetes. When administered it mimics caloric restriction and therefore has also been shown to extend lifespan. The exact mechanism by which metformin works to increase lifespan is not yet fully understood. It appears to operate on a number of pathways including decreasing IGF-1, inhibition of mTOR, reducing DNA damage, and influencing inflammation and autophagy and influencing digestion in the gut microbiome (12).
Studies have demonstrated Metformin’s ability to increase lifespan in mice (13, 14). Several studies have shown metformin may be beneficial for decreasing the incidence of cancer, improving cognitive function and increasing lifespan (15, 16, 17). More targeted studies in humans are currently being conducted.
Metformin can in most countries be purchased with a doctor’s prescription.
Stacking for increased benefits
Evolve Fitness recommends stacking a sirtuan activator (e.g. resveratrol) an NAD+ precurser (such as NMN or NR) and a senolytic (curcumin), these can safely be taken on a daily basis however we recommend periodically taking a break from all supplement regimes. If you are considering taking metformin for longevity purposes we recommend you speak with your doctor first.
References
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4509734/
2. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2016/press-release/
3. http://stm.sciencemag.org/content/9/377/eaai8700
4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/25881054/
5. https://medium.com/lifeomic/this-is-your-brain-on-fasting-a77d9d264de7
6. http://science.sciencemag.org/content/355/6331/1312
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29432159
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26485647/
9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22048312/
10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26840489/
11. https://www.ebiomedicine.com/article/S2352-3964(18)30373-6/fulltext
12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5943638/
13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18728386
14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21386129
15. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24985407/
Hacking aging - Part 1 Could you live to 150?
If you could take a pill that allowed you to live to 150 would you? Would the answer change if you could spend those years looking and feeling fit, young, healthy and disease free? Believe it or not science may be very close to making this possible.
If you could take a pill that allowed you to live to 150 would you? Would the answer change if you could spend those years looking and feeling fit, young, healthy and disease free?
Believe it or not science may be very close to making this possible. In this article we will discuss some of the most promising recent discoveries in anti-aging research and which of these are already available.
What is longevity or anti-aging really about?
Modern medicine has become very good at repairing many of our organs, and keeping our hearts and lungs functioning. However often our brains and muscles fail us and we spend a considerable portion of the end of our lives in suffering.
Longevity isn’t about just about living longer, it is about living better and spending less of our lives in a diseased or frail state.
The biggest driver of disease is aging. In fact, age is the biggest risk factor for lung cancer, many times more important than smoking! Age is a key risk factor in many diseases including cancer, heart disease and diabetes.
If we could wind back the body clock, we would greatly reduce the risk of all these diseases, and be able to lead fitter, healthier lives. David Sinclair, who leads Harvard’s anti-aging research would go one step further to say aging itself is a disease, and one that is curable.
Anti-aging is a relatively new and exciting area of study, most of the studies to date have been on yeast and mice however the results are promising. Scientists have already been able to significantly slow and even reverse aging in the lab in yeast, mice and monkeys. Human trials are also beginning.
In the first part of this two-part series we will discuss the recent anti-aging discoveries in blood borne factors.
Can young blood make you younger?
Credit: Villeda lab
In 2005, scientists at Stanford conducted a gruesome experiment whereby they surgically attached an older mouse to a younger mouse, so that they shared one blood supply. What they observed was this improved the ability for the old mouse to heal and regenerate, effectively making the old mouse appear younger again.
It is believed that somehow the blood from the younger mouse caused the stem cells from the older mouse to become more effective at repairing damaged cells and tissue in the older mouse.
This discovery led to some silicon valley start ups offering older patients blood plasma infusions from younger donors! However in February 2019 the FDA announced such services would require Investigational New Drug approval - this effectively put these companies out of service for the time being.
The Young Blood Institute is currently conducting a large scale trial of blood transfusions (rather than infusions). In a transfusion they replace aged plasma in older subjects with young plasma components form younger subjects. Blood transfusions are considered safer than infusions, as the total volume of blood in the patient remains the same. The trial began in 2018 and will continue over the next 2-3 years, or when the first 1,000 patients are completed, whichever comes first.
To date there have been no published results but the anecdotal reports have been promising. Several patients have reported improved memory, stamina, sex drive and improved feelings of well being.
If infusing the plasma from younger people sounds a little too gruesome for you, don’t be discouraged. Scientists are working to identify the factors within young blood which might be responsible for the positive effects. This would allow the individual factors to be isolated and delivered in a targeted medicine.
Blood consists of over 10,000 factors so it is a difficult task identifying the exact constituents responsible for the beneficial effects seen in the older mice, however a number of studies have already identified several constituents which seem promising. The most promising discoveries to date include GDF-11, TIMP-2, Oxytocin, and MANF, each of these is discussed in more detail below.
GDF-11 (Growth Differentiation Factor 11)
GDF-11 is a protein found in the blood of all mammals. A team at Harvard has claimed that the levels of GDF-11 in the blood of mice declines as the mice age, and therefore is more prevalent in younger mice. The team injected GDF-11 into older mice and was able to show that the muscle density in the older mice improved to youthful levels (1). The findings earned the team the award for scientific achievement of the year in 2014.
Several members from the Harvard team have since founded a company, Elevian which is investigating human applications of GDF-11 and other factors. They believe these factors may be able to restore the body’s natural regenerative capacity, to address a root cause of age-associated disease.
So far there have been no results from clinical trials where humans have been administered with GDF-11 however Biohacker Steve Perry has been self-experimenting with GDF-11 since 2014. Since 2014 Steve has enlisted over 100 volunteers in his study. This is not a double-blind placebo-controlled study so the results should be read with caution, but it is worth a look.
Steve Perry claims that many of the volunteers in his study reported improvements in blood pressure, heart rate variability, resting pulse rate, blood glucose, hand grip strength, reaction time, memory, eye sight, smell, hearing, and for some their grey hairs disappeared! (2)
GDF-11 is not FDA approved and the risks associated with supplementing GDF-11 in humans are not yet known, therefore we would caution against experimenting on yourself. In one study GDF-11 was shown to be damaging to the liver (3). To minimize risk the doses used by the participants in Steve’s study were extremely low (requiring dilution by a factor or hundreds of thousands) and the participants in Steve’s study closely monitored their vitals, and other biomarkers on a daily basis.
GDF-11 is available for purchase on the internet however rather than supplementing GDF-11 directly, you can boost it more naturally using regular exercise. People who exercise regularly over the long term demonstrate higher levels of GDF-11 then people who lead sedentary lifestyles (4).
TIMP-2 (Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2)
TIMP-2 is a human gene and protein. One study showed that injecting mice with blood plasma from a human umbilical cord, resulted in significantly improved cognitive function. Elderly mice that received the plasma were quicker to learn and remember the escape hatch location in a maze, they were better at learning associations between a room and an electric shock and faster making nests for their babies.
The team who conducted this experiment proposed this was due to TIMP-2. TIMP-2 levels start high when we are born and decline throughout life, similar to GDF-11.
When TIMP-2 was injected directly into the older mice they observed cognitive improvements similar to those mice that were injected with the umbilical cord plasma. Also when TIMP-2 was removed from the umbilical cord blood plasma before it was injected, no cognitive function improvement was observed (5).
The mechanism by which TIMP-2 works is not yet understood. A clinical trial to see if young human blood plasma can slow the cognitive decline of people with Alzheimer’s is being conducted. So far there are no studies assessing the safety of TIMP-2 supplementation in humans.
Sugars from the Aloe Vera plant have been shown to induce TIMP-2 production in the skin of rats when applied directly to wounds (6). Potentially Aloe Vera products may be able to increase TIMP-2 levels in humans, although this has not yet been demonstrated.
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a hormone produced in the body which plays a role in social bonding, sex and childbirth. It is often referred to as the ‘love hormone’. Oxytocin is released when we hug someone or hold their hand, it promotes feelings of trust, romance and friendship, it also increases libido. Oxytocin is released after birth to promote bonding with the baby.
Similarly to GDF-11 and TIMP-2, Oxytocin declines with age. One study demonstrated that Oxytocin has beneficial effects on maintaining healthy muscles and healing in old mice. Older mice who were injected with Oxytocin recovered faster from muscle injury than mice who were not treated with Oxytocin. The same study also demonstrated that when Oxytocin is blocked in young mice, their ability to repair muscles declined (7).
Unlike GDF-11 and TIMP-2, Oxytocin is already approved by the FDA for clinical use in humans. Pitocin is a synthetic form of Oxytocin used to help with childbirth. Also you can easily increase your own levels of Oxytocin naturally through a variety of activities including hugging, sex and, in women, nipple stimulation. Engaging socially, or playing with dogs has also been shown to increase levels of Oxytocin.
MANF (Mesencephalic Astrocyte-derived Neurotrophic Factor)
MANF is protein which is secreted by the body in response to stress. MANF is responsible for regulating metabolism and immune response. It also, like the other factors mentioned, declines with age.
In one study it was observed that MANF promoted the activation of immune cells which promoted neuroprotection and tissue repair (8). Researchers have also shown the same mechanism protects against liver damage in older mice and extends lifespan in flies.
Flies genetically engineered to express less MANF suffered from increased inflammation and shorter lifespans. Similarly older MANF deficient mice showed signs of bad health. When older mice shared a blood supply with MANF deficient younger mice, they did not see the benefits they would if sharing with younger normal mice (9).
There are several ways to increase your natural levels of MANF with the safest and easiest being fasting (10), and exposure to heat (e.g. via a sauna) (11).
Up next
In the second part of this series we will discuss some more practical approaches to anti-ageing, including fasting and various supplements which are readily available.
References
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23663781
2. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Oe9mDFRJFuk
3. https://www.fasebj.org/doi/abs/10.1096/fj.201800195R
4. https://physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.14814/phy2.13343
5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5586222/
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24491493
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4512838/
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27365452
9. https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-018-0023-6
Is a parasitic fungus the secret to athletic performance?
Cordyceps sounds like something out of a horror movie, it is a parasitic fungus that infects its host and devours it from the inside out, eventually killing it. However this parasitic fungus has been used for centuries in eastern medicine to improve performance and was at the center of a Chinese doping scandal. Could it be a powerful supplement to boost your athletic performance?
What is Cordyceps?
Cordyceps sounds like something out of a horror movie, it is a parasitic fungus that infects its host and devours it from the inside out, eventually killing it. Once it finishes consuming the hosts body, it sprouts a mushroom from the hosts head, and releases its spores to begin the whole cycle again with another host. Fortunately for us Cordyceps only infect insects.
What is it used for?
Cordyceps have long been used in traditional Chinese medicine to increase energy, treat asthma and improve sexual function. It is said that the benefits of Cordyceps consumption were first discovered when herders in the Himalayas observed that yak, goat and sheep which had eaten the mushroom became very strong and stout. The local people then used the fungus to improve the vitality of their cattle, and it was not long before the locals themselves started consuming it. The locals claimed it had aphrodisiac effects and it became known as Himalayan Viagra(1).
Cordyceps hit the headlines in 1993 during the Beijing Olympic games when several Chinese runners smashed various world records and attributed their success to eating Cordyceps mushrooms.
Wang Junxia beat the 10,000 meters women's world record by an astonishing 42 seconds, she also broke the 3000 meters world record and her teammate set a new world record in the 1,500 meters. It sounded too good to be true, could a mushroom do all this? Probably not.
Wang Junxia of China, center.
Credit Ed Reinke/Associated Press
Does it really work?
It appears this team may have been taking much more than mushrooms. In 2016 a letter reportedly from Wang and nine other athletes was published which alleged Coach Ma forced them to dope(2). In addition Coach Ma was fired from the Chinese national team in 2000 after 6 of his athletes tested positive for performance enhancing substances. However just because of this scandal the ability for Cordyceps to positively affect athletic performance should not be written off as several recent studies have shown some impressive results.
“Cordiceps has a significant positive effect
on athletic performance”
One human study showed that supplementation over a three week period (4 grams per day) resulted in significant improvements in the body's ability to absorb oxygen, improvements in exercise endurance and in some measures of heart health(3). Another study showed that exercise performance for healthy older people was significantly improved upon taking Cordyceps versus the placebo group (4)
The mechanism by which Cordyceps improves athletic performance is not fully understood but it is believed that Cordyceps helps improve blood flow as well as the body's ability to burn fat and process glycogen(5) (glycogen is the carbohydrate energy store within our muscles). Together these effects increase the availability adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the body, ATP is the source of energy the body uses to power the contraction of muscles.
In addition Cordyceps have been shown to delay lactate accumulation(6). Lactate accumulation is responsible for that burning feeling in muscles during intense exercise, consuming Cordyceps means you can exercise harder for longer.
But the benefits of Cordyceps are not limited to athletic performance; Cordyceps are also a powerful antioxidant(7), have been shown to help regulate the immune system(8), may help fight certain types of cancer(9) and may be beneficial for brain function(10).
It is important to note that most of the studies on athletic performance only observed benefits when supplementation continued for several weeks, very little benefit was shown from short term (one week or less) supplementation. Therefore if you choose to supplement with Cordyceps, you will need to keep it up for several weeks before you can expect to see results.
But not all Cordyceps are created equal!
The form of Cordyceps most commonly shown in pictures, where you see a mushroom sprouting out the head of a caterpillar is Cordyceps sinensis, it grows wild at high altitude in the Himalayas.
Cordyceps sinensis growing on caterpillars
Due to high demand and limited availability, wild Cordyceps now cost around $50,000 a kilo! Beware of any supplements which state they contain wild Cordyceps Sinensis, due to the high price tag these supplements often contain very little of the mushroom.
Fortunately there are other varieties of Cordyceps which can be grown in the lab which are far cheaper – and vegan friendly!
One of these is Cordyceps CS-4, Cordyceps Cs-4 is a mycelium culture which is grown in liquid vats, Cs-4 is unable to produce a mushroom but the mycelium which is cultivated has many of the same health benefits.
Another variety is Cordyceps militaris, which grows in Europe, and actually contains more cordycepin than the other species! Cordycepin is one of the constituents of Cordyceps which has anti-cancer, anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities(10).
Cordyceps militarism
Just beware of Cordyceps supplements which are grown on grain, often these contain mostly grain and very little of the mushroom or mycelium itself. Unfortunately it is not easy to identify such supplements but one red flag is if the label says anything like "myceliated brown rice/grain".
Unfortunately you won't find Cordyceps in your grocery isle but a range of supplements and extracts can be found online. Below is a selection of brands which offer products high in beneficial mycelium or mushroom content.
Another great way to get your daily dose of Cordyceps is to take it in your coffee or hot chocolate, the guys at Four Sigmatic produce some great mushroom blends.
References
https://www.nytimes.com/2016/02/25/world/asia/china-olympics-doping-ma-junren.html
Feng K, Yang Y. Q, Li S. P. Renggongchongcao. In: Li S. P, Wang Y. T, editors. Pharmacological Activity-Based Quality Control of Chinese Herbs. New York: Nova Science Publisher, Inc.; 2008. pp. 155–78.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1382668916300308
Can a pill make you smarter?
Can a pill make you smarter? It sounds like science fiction, but that is what many scientists are trying to achieve with nootropics. We examine how various nootropics work and examine some which have been shown to be effective for boosting memory, stamina, focus and motivation.
Can a pill make you smarter?
It sounds like science fiction, or the plot for a science fiction film, but it may be possible. Scientists have been exploring the potential for nootropics and other smart drugs to do just that.
What are nootropics?
The term “nootropics” is often used interchangeably with other terms such as “smart-drugs”, “brain boosters” or “cognitive enhancers’” The loosest definition of a nootropic is a compound which when ingested can enhance the cognitive activities of the brain. This definition is rather broad and if taken literally could include anything from Lavender oil to crack cocaine. Therefore for this article we shall use the definition provided by the man who coined the term “nootropic”, Dr. Corneliu E. Giurgea.
Dr. Giurgea stated that a nootropic must at least:
- Enhance memory and learning
- Help brain function
- Protect the brain
- Facilitate the transfer of information in the brain
- Be virtually non-toxic
The compounds which meet the definition above should, if taken in moderation, be safe for people to use on a regular basis. Other smart-drugs, such as Modafanil, or Adderall are potentially less safe to take on a regular basis and will be the topic of a separate article.
History of nootropics
Many traditional medicines have been used to improve cognitive function for centuries. For example Green Tea, Coffee and Ginko Biloba. However the modern exploration of nootropic research began in 1964 when Romanian psychologist and chemist Corneliu. E. Giurgea was developing the drug Piracetam to treat motion sickness.
Dr. Giurgea discovered Piracetam had cognitive benefits such as improved memory consolidation and information processing. This led Dr. Giurgea to officially coin the term nootropics in 1971.
Throughout the cold war the USSR started investing in nootropic research and it was a direct result of this research than many of the other popular nootropics were developed, in particular the other racetams such as Aniracetam, Oxiracetam and Pramiracetam.
Phenylpiracetam was developed in 1983 as a medication for Soviet Cosmonauts to help with prolonged stresses of working in space. It is considered a performance enhancing substance and banned in sports as it increases cold resistance and physical endurance.
Russian Olympic silver medalist Olga Pyleva was disqualified after 2006 Winter Olympics in Torino, Italy for using Phenylpiracetam.
Olga Pyleva was ultimately disqualified for using the nootropic Phenylpiracetam
Following the fall of the soviet empire the soviet research on nootropics was released and nootropics became more common in the west. However even to this day there is limited understanding of nootropics and their efficacy in the general population.
How do they work?
Nootropics work in a variety of ways, not all of them are fully understood, listed below are some of the common mechanisms of action.
Effecting neurotransmitters
In very simple terms neurotransmitters are the means by which neurons in our brains communicate. Many nootropics effect the level of neurotransmitters in the brain, thereby facilitating this communication.
Increasing energy
Some nootropics increase levels of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), ATP is one of our bodies preferred fuel sources. It is the fuel used to power the contraction of our muscles and is also a critical neurotransmitter in our brains.
Increasing circulation
Circulation is critical to a healthy brain. Some nootropics are vasodilators, meaning they open (dilate) the blood vessels, as a result blood flows more easily to the brain, delivering oxygen and nutrients to where it is needed.
Regeneration
Our brains are constantly repairing themselves and building new cells and connections, certain nootropics provide the brain with the ingredients it needs for this regeneration and growth.
Which ones work for what?
Below is a short selection of our favorite nootropics and the various purposes for which they are best suited – all based on scientific research.
For motivation - L-Tyrosine
L-Tyrosine is a non-essential amino acid, which is used to form dopamine and norepinephrine (1). In the brain dopamine functions as an extremely important neurotransmitter, in particular it plays a major role in the brains reward system which is responsible for driving motivation.
Norepinephrine is another important neurotransmitter, increased levels of which increases alertness, enhances memory and focuses attention. Interestingly the smart drug Adderall also works by increasing levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain.
Studies have shown L-tyrosene can be useful for improving mood (2) as well as for enhancing cognition (3).
For focus and clarity - L-Theanine
L-Theanine is an amino acid which is found in green tea. L-Theanine increases levels of serotonin, dopamine, and GABA in the brain. Some studies have shown L-Theanine increases alpha brain wave activity (4), which lowers anxiety and can therefore promote a feeling of relaxed attention.
L-Theanine works well when paired with a stimulant (such as caffeine). When combined with caffeine it has been shown to improve reaction time and working memory (5). L-Theanine helps “take the edge off” stimulants which can be particularly helpful to people with ADHD, or anyone prone to distraction.
For memory - Bacopa Monnieri
Bacopa monnieri is a herb which grows in wetlands around the world. It has traditionally been used in Ayurvedic medicine to prevent disease, promote longevity and strengthen the mind. Bacopa monnieri contains many alkaloids, flavonoids and saponins, it has been found to have adaptogenic and antioxidant properties.
The exact mechanism by which B. monnieri works is not fully understood however several studies suggest it has positive effects on memory. In a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study it was shown to significantly improve memory acquisition and retention in older healthy people (6). Other studies have produced similar results (7) (8).
For stamina - Rhodiola Rosea
Rhodiola rosea is a flowering plant which grows in arctic mountainous climates in Europe and Asia. Eastern Europeans have been using Rhodiola in traditional medicine for centuries to treat anxiety, fatigue and depression. It has also been used to traditionally to increase endurance and help with altitude sickness.
Rhodiola seems to work by blocking monoamine oxidases (9) which thereby reduces the breakdown of useful neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine.
There are not a lot of high quality studies on Rhodiola Rosea however there are several promising studies which demonstrate it may be effective in increasing the capacity for mental work against a background of fatigue and stress (10) (11).
The all rounder - Citicoline
Citicoline is a brain chemical that naturally occurs in the human body. It is used as a medication to treat Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, brain trauma, stroke victims, for age related memory loss, parkinsons and ADHD. In the United States it is sold as a dietary supplement but in many European countries it is a prescription only medication.
Citicoline provides the building blocks for both Phosphatidylcholine, one of the essential building blocks for neurons and cell membranes and Acetylcholine, which facilitates neuron to neuron communication.
Several studies have shown Citicoline is useful in producing improved attention and memory, especially in older subjects (12) (13).
Stacking for increased benefits
The benefits of nootropics are most pronounced when they are “stacked” or combined, especially when the mechanism of action for the various constituent compounds is different. When stacked the benefits can be accumulative.
The cheapest long term option is to buy your preferred nootropics separately in powder form and mix them yourself, however this is often not practical, especially for someone trying nootropics for the first time.
Buying a prepared blend not only delivers superior benefits but it eliminates the need to measure several pills and powders on a daily basis, and ensures the correct dosage. There are many companies selling nootropics over the internet, our preferred blend is Mind Lab Pro.
Mind Lab Pro is a true all rounder, containing all of the nootropics mentioned above. It is designed to improve memory, performance, mindset and provide building blocks for brain regrowth and repair. The only downside is it is a little expensive at approximately $65 for a 30 day supply.
References
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/026010618400300305
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/nogeikagaku1924/72/2/72_2_153/_article/-char/ja/
https://www.scirp.org/journal/PaperInformation.aspx?PaperID=19921#.VZrQM_lViko
Drugs and supplements for sexual performance
We examine various drugs and supplements which have been shown to increase libido, in men and women. Including Cabergoline, Bromocriptine, Mucuna Pruriens, Tribulus Terrestis, D-aspartic acid and L-Citrulline.
Whether you have low libido or are just looking to spice things up in the bedroom, this article may be for you. We will examine various drugs and supplements which have been shown to increase libido, in men and women.
Low libido affects around 15% of men and 32% of women (1). The leading causes of libido suppression include stress, anxiety, depression, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, and cholesterol. In addition, certain sex hormones decline with age, especially in men.
There are many lifestyle changes which can have a positive impact on sex drive, and these should be explored before considering drugs or supplements. Behaviors such as consuming a healthy balanced diet, exercising regularly, maintaining healthy levels of stress and anxiety and getting at least 7 hours of sleep a night can all can help with libido. However for those who have tried such changes or are still looking for an additional boost, there are a number of drugs and supplements which can be effective.
Most of the drugs and supplements which impact libido operate via one of 3 mechanisms of action; i) via dopamine and / or prolactin, ii) via androgenic hormones, or iii) through vasodilation.
The Dopamine / Prolactin connection
Dopamine and prolactin are closely linked to sex drive. It is theorized that dopamine increases sexual desire while prolactin reduces it, the link between dopamine and sex drive has been well established in men, but is less clear in women (2).
Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter, involved in many pathways in the brain. Dopamine is associated with motivation and concentration. Too much or too little dopamine can be detrimental, low dopamine can lead to Parkinson’s disease while abnormally high levels of dopamine have been linked to schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders.
Prolactin is a hormone, so named because it has a key role in milk production, however it also has over 300 other functions in the human body playing a key role in reproduction, metabolism, regulation of fluids, regulation of the immune system and influencing behavior.
Dopamine and prolactin appear to move in opposite directions, when dopamine is high, prolactin is low, and vice versa. Prolactin is produced after orgasm and it has been suggested that it may be responsible for the sudden change in mood many men feel after ejaculation.
As Dopamine is the incentivization hormone, it drives the desire to have sex, once the prolactin is released, dopamine levels fall and all of a sudden, the man is left wondering where the desire came from in the first place. This relationship can be observed in the chart below.
One study showed that the ability for some men to achieve multiple orgasms, may be attributable to reduced prolactin production in those individuals (3). This suggests that blocking prolactin could allow the average man to also achieve such states. In comes Cabergoline.
Cabergoline
The drug Cabergoline blocks the release of prolactin and has been shown to increase erections and libido in men (4). In one study, 60 healthy males normally needed a break of 19 minutes between orgasms. After taking cabergoline, they were able to have several orgasms within a few minutes.
Cabergoline has also been reported to increase the intensity of male orgasms (5). Another study showed Cabergoline can be effective in increasing sex drive in both men and women, who are suffering from elevated levels of prolactin (6).
High doses of Cabergoline can have unwanted side effects, some studies have shown it can increase the risk of heart failure, however at normal doses the risk appears low (7). Also some level of prolactin is desirable as prolactin supports neurogenesis (growth in brain tissue) so blocking it completely for a long time period is not recommended.
Bromocriptine
Bromocriptine works in a similar way to Cabergoline. Bromocriptine stimulates dopamine production and simultaneously reduces the levels of prolactin, although not by as much as Cabergoline. Bromocriptine has been reported by many men and women to have a powerful impact on sex drive.
Bromocriptine has been shown to increase libido in men recovering from dialysis treatment (8). Bromocriptine was also shown to increase sex drive in women suffering from high levels of prolactin (9).
Like cabergoline, bromocriptine, especially in high doses can have unwanted side effects such as high blood pressure, seizure or stroke. It is not recommended to take any of these medications without the supervision of a doctor.
Mucuna Pruriens – a natural dopamine precursor
A safer alternative to increase levels of dopamine would be so use a natural supplement, such as Mucuna Pruriens.
Mucuna Pruriens, otherwise known as Velvet Bean is a tropical bean native to Africa and Asia. It has been used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat snake bites and Parkinson’s disease. The seeds of the plant contain between 3-6% L-Dopa. L-Dopa is a precursor to dopamine and has the advantage of being able to cross the blood-brain barrier, whereas dopamine cannot. Once L-Dopa has entered the central nervous system it is converted to dopamine. L-dopa supplementation is therefore more effective than direct supplementation with dopamine.
Mucuna Pruriens is widely sold as a supplement to increase motivation, improve mood and as an aphrodisiac. Unfortunately there is limited research on its effects on sex drive in humans however it has been shown to increase sexual behavior in male rats (10).
The Androgenic compounds
Androgens are natural or synthetic steroid hormones which regulate the development of male characteristics. Androgens are produced in the human body in the testes, ovaries and adrenal glands. The main androgen hormone in men is testosterone. Although testosterone is mainly thought of as a male sex hormone, women also produce testosterone although at lower levels.
Testosterone plays a critical role in libido and sexual arousal in both men and women. Testosterone levels are often lower in people who lead sedentary lifestyles, have poor diets or lack sleep. Testosterone levels also decline naturally with age. Testosterone supplementation has been shown to increase libido in men and women with suppressed testosterone levels (11) (12).
Testosterone is widely used in high doses in the bodybuilding community.
Direct supplementation of testosterone can lead to unwanted side effects such as acne, hair loss, deepening of voice, facial hair growth and in women enlargement of the clitoris – however these tend to only occur at higher doses such as those used for bodybuilding. In addition supplementing exogenous testosterone can inhibit the body’s natural production mechanism, making the problem of low testosterone worse once you stop supplementing.
Due to the side effects we would recommend avoiding direct supplementation with testosterone and rather suggest raising levels naturally through improved sleep, diet and exercise. If these factors alone aren’t sufficient you can try supplementing with Tribulus Terrestis or D-aspartic acid.
Tribulus Terrestis
Tribulus Terrestis is a small leafy plant which grows in Europe, Asia, Africa and the Middle East. The root and fruit of the plant have been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurvedic medicine for a variety of purposes, including increasing libido.
The jury is still out on how effective Tribulus is at increasing testosterone levels, however it has shown promise in some studies in women. One study of postmenopausal women with low libido found that supplementation with Tribulus over a 120 day period increased levels of testosterone and sexual desire (13). However other studies have not been able to back up these findings, especially in relation to the broader population (14).
D-aspartic acid
Another supplement which may be effective at increasing testosterone levels is D-aspartic acid. D-aspartic acid is a naturally occurring amino acid and it is important for brain and nerve development, as well as the development of testosterone.
However again the research findings are mixed. It seems D-aspartic acid is most effective at raising testosterone levels in non-resistance trained men (15). Studies in active resistance trained men found supplementation either had no effect or even reduced testosterone levels (16) (17) (18), therefore we would recommend supplementation only in individuals with suppressed testosterone levels and relatively inactive lifestyles.
There is no real research available on the efficacy of D-aspartic acid in women however as it works via stimulating the testes, it is unlikely to have the same effects for women.
Vasodilators
Another class of supplements works by increasing circulation, typically by increasing levels of nitric oxide. These compounds have less of an effect on sexual motivation but can improve erections in men and sensation in both men and women.
Nitric oxide (NO) is a molecule produced naturally in the body. NO is responsible for vasodilation, increased levels for NO cause the inner muscles of blood vessels to relax, which causes them to widen, thereby increasing circulation. The link between NO and erections is well established (19). Sildenafil (Viagra) works by inhibiting the enzyme which is responsible for breaking down NO in the genitals, thereby improving circulation in this area.
Viagra (Sildenafil) is a powerful vasodilator.
L-Citrulline
For anyone not wanting to take drugs such as Viagra another option is L-Citrulline. L-Citruline is an amino acid which is produced naturally in the body and is also found in various foods, including watermelon. L-Citriline has been shown to increase NO synthesis, thereby improving circulation (20). Supplementation with L-Citriline has been shown to improve erections in patients experiencing mild erectile dysfunction (21).
In conclusion
The causes of low libido can vary significantly from individual to individual, therefore no one treatment will work for everyone. The best approach is to ensure a healthy lifestyle with low stress, plenty of sleep and exercise and a healthy, balanced diet. For those looking for an additional boost a mixture of herbal remedies such as mucuna pruriens, Tribulus, D-aspartic acid and L-Citriline may help.
References
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2695750/
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7770195
3. https://www.nature.com/articles/3900823
4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14656205
5. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/1949087.stm
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29746287
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5240058/
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6357576
9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29475005
10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20456630
11. https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/91/7/2509/2656285
12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2673004/
13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27760089
14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26727646
15. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19860889
16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25844073
17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28841667
18. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24074738
19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8248281
14 ways to improve your sleep
A good night’s sleep is one of the most important things you can do for your overall health, arguably more important than diet or exercise. Poor sleep has been linked with weight gain, heart disease, increased risk of infection, diabetes, reduced sex drive, memory problems, cancer, depression and ultimately death!
7/10 people have difficulty sleeping at least one night per week (1). If you are reading this article then chances are you do too.
A good night’s sleep is one of the most important things you can do for your overall health, arguably more important than diet or exercise. Poor sleep has been linked with a range of health problems including weight gain (2), heart disease (3), increased risk of infection (4), diabetes (5), reduced sex drive (6), memory problems and Alzheimer’s (7), cancer (8), depression (9) and ultimately death (10)!
This article outlines various methods which have been shown to improve sleep. Unfortunately there is no one-size-fits-all solution however experimenting with various approaches below should help you get a better nights rest.
Fix your diet
Avoid sugar
High sugar intake has been associated with lighter, less restorative sleep and more awakenings during the night (11). This can lead to a viscous cycle, when people are tired from lack of sleep, they tend to crave more junk food, so the cycle repeats (12). Try to avoid foods high in refined
sugar, especially before bed.
Avoid spice
Spicy food may also be a culprit in keeping you awake. Not all spicy food is to blame (some spices may help promote sleep) but chili and mustard have been shown to raise body temperature, which is the enemy of sleep.
The active ingredient capsaicin is the culprit (13). In addition too much spicy food can cause gastric disturbance, indigestion and can leave you feeling restless throughout the night.
Avoid alcohol
A glass of red wine might make you feel sleepy, and indeed alcohol can help people to fall asleep but several studies have shown alcohol reduces REM sleep. REM sleep is the stage of sleep when you are dreaming, and it is thought to be the restorative phase of sleep.
Alcohol also causes dehydration, and releases toxins into the body which can make you feel even worse in the morning.
In one study as little as one drink was shown to impair sleep quality. Moderate alcohol consumption lowered restorative sleep quality by 24% and a high alcohol intake by as much as 39% (14).
Change your behavior
Don’t do this!
Eliminate screens
Cell phones, television screens and computers all emit blue light. Blue light has been shown to reduce our body’s natural production of the sleep inducing hormone, melatonin.
A study of screen use before bed found screens emitting more blue light led to poorer sleep outcomes (15).
If you need to use a screen before bed,
try to activate the blue light filter, or wear
blue blockers (described below).
Try meditation
Is a racing mind keeping you up at night? Oftentimes when we lie in bed we start replaying the days events or we start worrying about the future.
Meditation helps focus the mind on the present, it helps us acknowledge and realize the thoughts and emotions which are causing us stress and anxiety.
It has been shown that meditation helps slow breathing and lower the heart rate (16), both of which help the body relax and fall asleep. Mindfulness meditation has been shown to be an effective way to promote sleep (17).
If you are new to meditation I suggest using a guided meditation, you can find a number guided meditations on YouTube or through apps such as Headspace, or Waking Up.
Read a book
Reading, like meditation refocuses the mind away from stressful thoughts and anxieties.
One study showed that reading a book for only 6 minutes reduced stress levels by 68% (18), which was more than listening to music, drinking tea or going for a walk.
Reading is also a good substitute for television and social media, which have been shown to expose viewers to blue light which is responsible for keeping them awake.
Change your environment
Reduce lighting
When humans are exposed to blue light, the body ceases to produce melatonin. This can disrupt the body’s natural sleep cycle, otherwise known as the circadian rhythm. Exposure to blue light signals to the body that it should be awake. In one study exposure to even a dim light at night
was associated with decreased total
sleep time and sleep efficiency (19).
At least 2 hours before bed try to turn off as many lights as you can, use dim bulbs where possible and when sleeping try to eliminate all sources of light (cover any light coming from digital displays) and use blackout curtains if you have light coming from the window.
Control the temperature
A small change in temperature can have a drastic impact on sleep quality. A cooler environment can help promote sleep.
Interestingly when humans sleep our CORE body temperature drops, but our skin temperature actually increases. This happens because higher
skin blood flow helps helps cool the body.
One way to lower your core body temperature is to lower the temperature in your bedroom, also avoid strenuous exercise before bed. if you want to take it to the extreme, you can go to bed wearing nothing but socks and gloves! This can actually help lower your core temperature as it will stimulate the body to push blood to your extremities to stay warm, this will increase your skin temperature while cooling your core, it may look strange but it works.
Eliminate abrupt noise
Environmental noise is a significant cause of sleep disruption, the WHO published guidelines in 2009 stating that annual average night noise exposure should not exceed 40 decibels, similar to a quiet street in a residential area. Anyone exposed to higher levels than this is at risk from
adverse health effects (20).
Try to eliminate sources of noise where possible, if this can’t be done try earplugs or play some white-noise, white noise (as opposed to abrupt noises) can actually help calm the mind and promote restful sleep.
Try supplements
Melatonin - For jetlag
Melatonin is a hormone found naturally in the body, the primary responsibility of this hormone is to regulate our sleep-wake cycles. Melatonin levels rise in the body when darkness occurs, causing us to feel sleepy. Melatonin levels stay elevated during the night and fall to almost zero during the day.
One of the causes of jetlag is a disruption in the sleep-wake cycle. If jetlag is making it difficult to fall asleep then taking a melatonin at bedtime can help shift the sleep cycle earlier. Inversely if jetlag is causing you to wake early, taking melatonin upon waking can help you fall back to sleep and will also shift your sleep cycle later. The same is true for shiftworkers with disrupted sleep cycles.
Studies have shown melatonin can be an effective treatment to adjust the timing of sleep cycles in those affected by jetlag (21), and possibly for the treatment of insomnia. As a generic sleep aid for someone not experiencing jet lag or sleep cycle disruption melatonin has not been shown to be effective.
Glycine - For those looking for a mental boost
Glycine is an amino acid which your body uses to create proteins, the body naturally produces glycine from other amino acids and Glycine is found in protein rich foods. Glycine is also available as a dietary supplement.
It is believed Glycine induces sleep by reducing core body temperature, it does this by dilating the blood vessels in the periphery of the body, which results in heat loss (22). During a normal sleep cycle, sleep usually occurs when our core temperature is dropping, as it would after glycine supplementation.
Glycine has been shown to not only improve sleep quality but as a bonus it has also been shown to improve feelings of daytime sleepiness and improve performance of memory recognition tasks (23).
Valerian root - For the light sleeper
Valerian is a herb which is native to Europe and Asia, an extract of the root of the plant is commonly sold as a dietary supplement to promote sleep. Valerian has been used as a medicinal herb to since Ancient Greece.
Many of the studies on valerian remain inconclusive and the exact mechanism by which valerian has its effects are not fully understood. It is believed that Valerian acts on the GABA receptors in the brain, similar to benzodiazepines (a commonly prescribed class of drugs for sleep and anxiety) (24).
A recent meta analysis of the various studies examining valerian as a sleep aid concluded that valerian might improve sleep quality (25).
Try these wearables
The Manta Sleep Mask takes it to a new level
Eye mask & earplugs
Noise and light can be very detrimental to sleep quality. Even if we are not fully woken background noise or residual light from a street lamp, clock radio or even the morning sun can significantly lower sleep quality. One study of patients in an intensive care unit showed that the use of earplugs and eye masks resulted in significantly more REM sleep, less
awakenings and elevated melatonin levels (26).
Felix Gray makes some trendy blue light blockers without the ugly orange lenses
Blue light blockers
Our bodies natural sleep cycles (the circadian rhythm) is regulated by the production of melatonin in the human body.
Studies have shown that melatonin production is suppressed when humans are exposed to blue light. In the natural world this makes sense, the sun goes down and the human body starts producing melatonin which helps induce sleep. Unfortunately today we are surrounded by artificial lighting which inhibits our bodies natural production of melatonin. In addition some studies suggest a link between exposure to light and an increase risk of cancer, diabetes, heart disease and obesity (27).
Wearing blue light blocking glasses in the evening for a few hours before bed is one way to fool the brain into producing melatonin again. Wearing glasses in the evening may look strange but it’s probably a better option than lighting your whole apartment like a brothel.
References
https://www.consumerreports.org/sleep/why-americans-cant-sleep/
https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2013/03/06/1216951110.abstract
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006899311014302
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/1788611
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/107/1/43/4794751#112507111
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/07420528.2017.1324878
https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/meditation-offers-significant-heart-benefits
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2110998
https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/health/news/5070874/Reading-can-help-reduce-stress.html
health/noise/publications/2009/night-noise-guidelines-for-europe
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1111/j.1479-8425.2007.00262.x
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/blue-light-has-a-dark-side