RECENT
NAD Patches - Do they work?
We explore what are NAD patches, how do they work and what are the potential benefits, if any.
Introduction
NAD, or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. It plays a key role in a range of biological processes, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular signaling. In recent years, there has been growing interest in the use of NAD patches as a way to increase NAD levels in the body. In this article, we will explore what NAD patches are, how they work, and their potential health benefits.
What are NAD Patches?
NAD patches are transdermal patches that contain NAD precursors, such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). These precursors are converted into NAD in the body, increasing the levels of this important coenzyme.
How do NAD Patches Work?
NAD patches work by providing the body with NAD precursors, which are converted into NAD in the body. NAD is a critical coenzyme involved in a range of biological processes, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular signaling. By increasing NAD levels in the body, NAD patches may offer a range of potential health benefits.
Potential Health Benefits of NAD Patches
Improved Energy Metabolism: NAD is involved in energy metabolism, helping to convert food into energy that can be used by the body. By increasing NAD levels in the body, NAD patches may help to improve energy metabolism, potentially leading to increased energy levels and improved athletic performance.
Anti-Aging: NAD has been shown to play a role in aging, with declining NAD levels being associated with a range of age-related conditions. By increasing NAD levels in the body, NAD patches may help to slow the aging process, potentially reducing the risk of age-related conditions like Alzheimer's disease and cardiovascular disease.
Improved Cognitive Function: NAD has been shown to play a role in cognitive function, with declining NAD levels being associated with cognitive decline. By increasing NAD levels in the body, NAD patches may help to improve cognitive function, potentially reducing the risk of conditions like dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
Improved Exercise Performance: NAD has been shown to play a role in exercise performance, with declining NAD levels being associated with reduced endurance and muscle function. By increasing NAD levels in the body, NAD patches may help to improve exercise performance, potentially leading to increased endurance and muscle function.
Potential Treatment for Neurological Disorders: NAD has been shown to have neuroprotective effects, potentially offering a treatment option for neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis. By increasing NAD levels in the body, NAD patches may help to protect against neuronal damage, potentially reducing the risk of these conditions.
Conclusion
NAD patches are transdermal patches that contain NAD precursors, such as NR or NMN. By providing the body with these precursors, NAD patches may help to increase NAD levels in the body, potentially offering a range of health benefits, including improved energy metabolism, anti-aging effects, improved cognitive function, improved exercise performance, and potential treatment for neurological disorders. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of using NAD patches.
Sources:
Braidy, N., Berg, J., Clement, J., Khorshidi, F., Poljak, A., Jayasena, T., ... & Sachdev, P. (2021). Role of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and related precursors as therapeutic targets for age-related degenerative diseases: rationale, biochemistry, pharmacokinetics, and outcomes. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling
Long, A. N., Owens, K., Schlappal, A. E., Kristian, T., Fishman, P. S., & Schuh, R. A. (2015). Effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide on brain mitochondrial respiratory deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease-relevant murine model. BMC Neurology, 15(1), 19. doi: 10.1186/s12883-015-0272-x
Mills, K. F., Yoshida, S., Stein, L. R., Grozio, A., Kubota, S., Sasaki, Y., ... & Imai, S. (2016). Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice. Cell Metabolism, 24(6), 795-806. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013
Moreno-Sánchez, R., Rodríguez-Enríquez, S., Marín-Hernández, A., & Saavedra, E. (2007). Energy metabolism in tumor cells. The FEBS Journal, 274(6), 1393-1418. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05686.x
Sinclair, D. A. (2013). Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD+ intermediate, treats the pathophysiology of diet-and age-induced diabetes in mice. Cell Metabolism, 17(6), 819-831. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.04.005
Yoshino, J., Mills, K. F., Yoon, M. J., & Imai, S. (2011). Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD+ intermediate, mediates age-associated mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. Cell Metabolism, 10(6), 668-676. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.10.012
GHK-Cu - a treatment for skin aging?
GHK-Cu us a copper peptide which is naturally occurring in the human body. The level of GHK-Cu in our bodies declines as we age. Studies suggest GHK-Cu may be beneficial in promoting wound healing, boosting immunity, reducing inflammation and promotion of skin repair. Due to these purported benefits GHK-Cu is a strong candidate for anti-aging therapy.
GHK-Cu is a copper peptide which is naturally occurring in the human body.
A peptide is a small molecule made of amino acids. Peptides are precursor components of proteins.
Peptides are able to mimic signals from the brain to stimulate the body into various processes. For example the presence of a certain peptide may signal the body to stimulate skin repair.
The level of GHK-Cu in our bodies declines as we age. Studies suggest GHK-Cu may be beneficial in promoting wound healing, boosting immunity, reducing inflammation and promotion of skin repair. Due to these purported benefits GHK-Cu is a strong candidate for anti-aging therapy.
Dr. Loren Pickart
GHK-Cu was discovered in 1973 by Dr. Loren Pickart who has his own brand of copper peptide cosmetics called Skin Biology. Dr Pickart discovered that GHK-Cu assisted in wound healing and had anti-inflammatory properties, this led to the development of Iamin Moustirizing Gel – a treatment used for wounds.
Today GHK-Cu can be purchased in pure form from several peptide manufacturers. It can also be found in some specialty cosmetics, however it is rather expensive to produce so is still rather rare.
Benefits of GHK-Cu supplementation
For wound healing
GHK-Cu has been found to enhance wound healing in rats and rabbits. In several studies GHK-Cu cream was applied topically to wounds and it was shown to significantly reduce heling time (1) (2).
A similar effect was also demonstrated in humans. In diabetic patients, treatment with a topical GHK-Cu gel sped the healing of plantar ulcers (3).
Interestingly GHK-Cu injected in one area of the body has also been shown to improve healing at distant body areas. For example GHK-Cu can be injected in the thigh to assist with healing throughout the body (4).
Anti-inflammatory effects
Inflammation is one cause of aging, as discussed in our article on the causes of aging. GHK-Cu has an anti-inflammatory effect. The mechanism of action is not fully understood but GHK-Cu may help reduce signs of aging and also provide a credible substitute for corticosteroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to fight inflammation (5).
GHK for the skin
In several studies GHK-Cu seems to be beneficial in reversing signs of aging in skin. GHK-Cu seems to increase the ability for skin sells to survive and multiply – this can help with skin repair, regeneration, elasticity and thickness.
GHK-Cu seems to improve production of skin stem cells, it increases collagen integrity, it reduces scarring (be breaking down large collagen deposits and replacing them with finer deposits. it also protects against photodamage (6) (7) (8).
In one study twice daily application of GHK-Cu to the facial skin of 40 women aged 40 to 65. The trial was run over 8 weeks and the treatment was found to significantly reduce wrinkle volume and wrinkle depth compared to control serum (9).
GHK for Hair Growth
GHK-Cu has also been found to stimulate hair growth and potentially darken pigments in hair (prevents greying) (10).
Cognitive Benefits
GHK-Cu has been shown to stimulate nerve regeneration. This may be beneficial in preventing or reversing cognitive decline. In one study GHK was shown to increase production of nerve growth factors and the rate of regeneration of nerve fibers (11).
How to take GHK-Cu
We recommend using GHK-Cu containing creams topically. It’s also under the 400 Dalton molecular weight threshold which makes it suitable for topical and transdermal delivery. This is safer than injections and seems to be the more effective method for prevention of skin aging. The chosen cream should not be in excess of 1% GHL-Cu, stronger formulations may be counterproductive.
Products containing GHK-Cu
As GHK-Cu is expensive to produce you should go with a reputable supplier. Make sure you check the color of the product also. Any GHK-Cu cream containing 1% or more GHK-Cu should be bright blue in color.
GHK-Cu is bright blue due to the copper present
Skin Biology
Dr Loren Pickart who discovered GHK-Cu has his own company which sells various creams containing GHK-Cu. The branding of the site is not very sexy but it is one of the cheapest formulations available and a very reliable formulation.
The Ordinary (A Deciem brand)
The Ordinary produces the “Buffet” + Copper Peptides 1% serum. Which contains GHK-Cu with a range of other peptides and Hylauronic Acid. At Around $30 for 30ml it is reasonably priced.
NIOD (A Deciem brand)
Deciem produces the NIOD range which contains GHK-Cu in a variety of formulations. NIOD is well formulated, branded and has good reviews but at over $100 for a 15ml tube it is rather expensive.
REFERENCES
1) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14648529/
2) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17083573/
3) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17147644/
4) https://patents.justia.com/patent/5164367
5) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23285694/
6) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23019153/
7) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19319546/
8) https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.elsevier-f015a350-2cce-3361-99cf-79290da3bb45
10) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8326148/
11) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15703015/
APPLICATION OF STEM CELL TECHNOLOGY FOR ANTI-AGING
Stem cell therapies are becoming increasingly popular for anti-aging. Celebrities and middle age business men and women are flocking to exotic locations to inject themselves. But is this all in vain? In this article we will discuss the various applications of stem cells in anti-aging, and the efficacy of each approach.
Stem cell therapies are becoming increasingly popular for anti-aging. Makeup, moisturizers and face masks line the shelves touting the benefits of various “stem cell” formulations. Celebrities and middle age business men and women are flocking to exotic locations to inject themselves with stem cells sucked from their belly fat. Is this all in vein or is there some credible science behind this?
Stem cells show a lot of promise for the treatment of aging and various age-related diseases but the science is new and there are very few high quality studies. In addition, there are many different formulations and delivery methods, each of which is not equally effective.
In this article we will discuss the various applications of stem cells in anti-aging, and the efficacy of each approach.
WHAT ARE STEM CELLS?
Stem cells are cells which have the ability to divide and transform into other types of cells. They are involved in building every type of tissue in the human body. This is why stem cells have great potential for therapeutic uses in tissue regeneration and repair.
Unfortunately, the number and function of stem cells in our bodies declines with age, this is one of the reasons why our bodies natural healing and repair processes decline with age, and is a contributing factor to many age-related diseases.
THERE ARE SEVERAL TYPES OF STEM CELLS
Pluripotent stem cells could become any type of cell in the body. For example, embryonic cells are pluripotent and can become stomach, lung, skin, or brain cells.
Multipotent stem cells develop into different specialized cells of a specific tissue. Unlike pluripotent cells, the fate of multipotent cells is limited. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are an example of multipotent cells that can develop into bone cells, cartilage cells, and muscle cells. MSCs are currently very significant in stem cell therapy because they can readily be harvested from adult donors, unlike the other types of cells.
Unipotent stem cells have the ability to become only one type of cell. For example, the satellite cells of the skeletal muscle are limited to becoming mature skeletal muscle cells.
VARIOUS DELIVERY METHODS OF STEM CELLS
When treating patients for injury or anti-aging purposes there are a variety of stem cell delivery methods, some of the most common approaches are:
Direct injection
This is where the stem cells are injected directly into the site which is being targeted. For example, for arthritis the stem cells would be injected into the affected joint. Or for facial aging, the cells might be injected into the surface of the skin. While there is limited evidence, direct injection of stem cells appears promising.
Grafts
In a graft a bio scaffolds is created to function as a porous and permeable solid structure for stem cell attachment, growth, and migration. This scaffold is then surgically inserted into the site of injury. While there is limited evidence, grafts appear to be a promising method for delivering stem cells to facilitate repair in problem areas.
IV
Some treatments deliver stem cells intravenously. Some doctors claim that the stem cells will be able to target the problem areas in the body and deliver systemic anti-aging benefits. Unfortunately, the evidence to back up this claim is lacking, most stem cells which are injected intravenously end up trapped in the lungs, liver and kidneys (1).
Topical Creams
Some products such as face creams and masks claim they contain stem cell formulations which can be topically applied. There is no evidence that such a formulation would be beneficial as stem cells will not survive in this environment.
ARE STEM CELLS EFFECTIVE FOR ANTIAGING?
Aging is leading risk factor for many diseases, one of the primary causes of diseases like arterial atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, is the decline in the self-repairing capabilities of our cells as we age. A decline in the rate of cell division and the rate at which stem cells transform into other types of cells is a characteristic of aging. This decline in cell division reduces our ability to repair tissues and maintain organs as we get older. Therefore, stem cell technology is a likely candidate to slow or even reverse the aging process.
Stem cell treatments have shown promise in promoting our bodies self-repairing capability, and therefore could have powerful anti-aging benefits. As stem cells replace our damaged or non-functioning cells, they help us maintain normal function of our tissues and organs (2) (3).
Stem cells are also known to secrete various biologically active proteins such as growth factors, cytokines and other proteins that are important in cell signaling and vital immune function. This plays a very important role in tissue regeneration. For example, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can secrete signal protein - vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) that stimulates the formation and regeneration of blood vessels. This provides a big advantage for elderly body's ability to repair and regenerate especially because it's more prone to certain diseases (4).
WHAT ARE THE RESULTS SO FAR?
For Longevity
There currently are no conclusive studies in humans demonstrating that stem cell treatments can increase lifespan, however studies in mice show some promise. In one study stem cells were intravenously transplanted to 10-month-old rats once a month throughout their lives. This led to cognitive and physical improvements and their life span was extended by between 23% and 31% (5).
Caution should be exercised when extrapolating these results to humans. These rats were given very large doses and they were given repeatedly throughout their lifetime. In humans the vast majority of stem cells delivered intravenously end up trapped in the lungs, liver and kidneys, very little makes its was to other vital organs such as the heart and brain. In addition, it is not feasible nor affordable for most people to get treatment every month for the rest of their lives.
FACIAL AGING
The production of collagen starts to decline as we age which leads to wrinkles and sagging skin. One study has shown that many small injections of the stem cells just below the surface of the facial skin led to significant improvements in several markers of skin aging. Stem cells helped with formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones, survival of the cells & their division, boosted immune response and they helped with overall collagen degradation (6).
In addition, fat-derived stem cells are often used in plastic surgery as seed cells. They play important role in prevention of photoaging (premature aging of the skin caused by repeated exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UV) – sun light). As we age, melanocytes (cells that synthesize skin pigment - melanin) become victim to excess sun exposure, inflammation and hormonal changes which can lead to development of unsightly dark spots and hyperpigmentation. This therapy has been shown to help with these aging symptoms.
FOR THE BRAIN
The function of neural cells in our brains declines with age. Aging in the central nervous system is associated with progressive loss of function which is exacerbated by neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
Cell therapy may be able to replenish lost cells and restore brain function. There are two primary strategies to achieve cell replacement. The first is transplantation of exogenous stem cells and the second is stimulating the body’s own activation of its neural stem cell population (7).
As most people would not risk injecting stem cells into their brains for potential anti-aging benefits these experimental treatments are reserved for only the most serious brain injuries. However, stimulating the body’s own production of stem cells may be beneficial, this can be done via supplements which are outlined in our anti-aging guide. (8)
FOR THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
It is well established that our immune system becomes less effective as we age. The decline in immune function which we experience with age, is partly due to the loss in efficacy of our bodies blood cells, largely as a result of decreased production of certain blood cells know as B and T lymphocytes. This can lead to various diseases including cancer.
Hematopoietic stems cells (HSC's) are stem cells which give rise to other blood cells. Some research has suggested that reconstituting HSC or pluripotent stems cells may rejuvenate the supply of stem cells and help boost our immune systems (9).
HSC’s have been used to boost the immune systems of cancer patients for years via bone marrow transplants, however this treatment should only be reserved for extreme life-saving cases and is not suitable for anti-aging purposes.
A safer alternative may be rejuvenating our existing stem cell populations, this could be achieved through NAD+ supplementation (see our anti-aging report).
SKELETAL MUSCLES
One of the reasons our muscles can repair so quickly is we have a very large pool of stem cells in our muscles. As we age, we experience a loss of muscle function partly as out muscle stem cell pool is depleted.
Some therapies have been shown to restore the ability of muscle stems cells to rejuvenate. One of these treatments is NAD+ recruitment as mentioned in our anti-aging report. Supplementation with NAD+ precursors like NR can help protect from the loss of muscle stem cells, this has been demonstrated this effect in mice (10).
FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS
In clinical trials stem cells have been used to regenerate cartilage and safely treat Osteoarthritis (OA). Stem cells can have beneficial effects in regulating the microenvironment of damaged tissue, leading to more favorable conditions for tissue regeneration. Stem cells have been used in cell therapy to promote the repair of cartilage, muscle, and bone.
There was no serious side effects demonstrated however due to regulatory issues in the US only Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF), a cellular extract that is made in a laboratory from fat is currently approved for clinical uses in humans. SVF only contains a small amount of stem cells (11).
STEM CELL THERAPY – COST, BENEFITS & SIDE EFFECTS
Stem cell therapy can cost anywhere between $500 to $50,000.
The cost depends on many variables such as the type of stem cells that are being used, where you are performing the treatment, where the laboratory is located, and if the cells that are being used are ethically sourced & regulated.
SIDE EFFECTS & RISKS
Some serious side effects that can occur include:
Administration site reactions
The ability of cells to move from placement sites and change into
inappropriate cell types or multiplyFailure of cells to work as expected
The growth of tumors.
Unproven stem cell treatments can be unsafe, so remember - make sure to do your research and ask as many questions as you can before you to commit to an actual treatment. If you are considering treatment in the United States, ask your health care provider if the FDA has reviewed the treatment.
CONCLUSION
The results from clinical trials and studies have demonstrated that stem cell have great potential for regeneration medicine and help with age-related problems such as slower regeneration time and degradation of our tissues. However, stem cell treatments are still regarded as experimental in the US. With further development of stem cell technology, it is only a matter of time before it becomes an effective treatment for aging-related diseases and offer new kind of alternatives for antiaging.
Being treated with stem cells is also not without significant risks, including the potential to cause cancer. Therefore, restraint is advised. Stem cell therapies should only be considered where other options are not effective. If you choose to have a stem cell treatment make sure you go to an approved and accredited facility. Also, it is best to consider treatments which have already shown some promise such as site injections or scaffolds, avoid anyone touting the benefits of a systemic intravenous injection.
REFERENCES
1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5260805/
2) Tsang SH (2013) Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine in ophthalmology. Springer, New York
3) Somasundaram I (2014) Stem cell therapy for organ failure. Springer, New Delhi
4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25797907
5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26315571
6) https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7315830
7) https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2002.tb00451.x
8) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41536-017-0033-0
9) https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2014-0132
Stem Cell Therapy for Sports-Related Injuries
In the last 5 years, we have seen an increasing number of professional athletes turning to stem cell therapies to recover from injury. Tiger Woods, Rafael Nadal, and Max Scherzer have all been reported to have undergone stem cell therapy for their sports-related injuries.
While stem cell therapy was once prohibitively expensive for most, prices have come down significantly, making it more accessible. In this article we will discuss what stem cells are, the various treatments available and their efficacy and cost.
In the last 5 years, we have seen an increasing number of professional athletes turning to stem cell therapies to recover from injury. Tiger Woods, Rafael Nadal, and Max Scherzer have all been reported to have undergone stem cell therapy for their sports-related injuries.
While stem cell therapy was once prohibitively expensive for most, prices have come down significantly, making it more accessible. In this article we will discuss what stem cells are, the various treatments available and their efficacy and cost.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are cells in the body that have the potential to self-renew, develop into other types of cells, or divide into identical cells. When there is an adequate source of resources and the right environment, stem cells have the ability to change and become cells with highly specialized functions. Moreover, stem cells are the cells that are responsible in tissue repair and injury recovery in the muscles, liver, kidneys, and lungs (1). There are several types of stem cells:
Pluripotent stem cells could become progenitors of any type of cell in the body. For example, embryonic cells could become stomach, lung, skin, or brain cells.
Multipotent stem cells develop into different specialized cells of a specific tissue. Unlike pluripotent cells, the fate of multipotent cells is limited.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are an example of multipotent cells that can develop into bone cells, cartilage cells, and muscle cells. MSCs are currently very significant in stem cell therapy because they can readily be harvested from adult donors, unlike the other types of cells.
Unipotent stem cells have the ability to become only one type of cell. For example, the satellite cells of the skeletal muscle are limited to becoming mature skeletal muscle cells (2).
What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy is a treatment approach that utilizes stem cells grown in the laboratory. These cells are used to replace lost tissues or to assist existing tissues in performing specific functions.
Current techniques of stem cell therapy commonly utilize MSCs because they can be derived from various adult organs and tissues, making it easier to be acquired as compared to pluripotent cells. MSCs can be harvested from the placenta, fat cells, liver, lung, or blood vessels (3).
Stem cells are first harvested or isolated from the donor tissue. The cells are then grown or cultured in the laboratory. When successfully cultured, stem cells are then injected to the recipient and are expected to home to the target organ, in most cases, to the injured site. The recipient is then monitored for possible inflammatory reactions following the injection of stem cells (3).
Stem cell therapy for injury repair
The US Department of Health and Human Services estimates that the average annual number of sports and recreation-related injuries is at 8.6 million per year (4). The ability of MSCs to become mature bone, cartilage, or and other connective tissues make them ideal sources of regenerative tissues for injury repair, especially for sports-related injuries. MSCs could function as regulators of growth and maintenance in these tissues (1). In addition, MSCs release different substances that stimulate the existing cells in the injured tissue to undergo cell division, hence increasing the number of cells and promoting tissue survival (5).
Current regenerative medicine techniques for sports-related injuries include 3 methods:
· Platelet-rich plasma
· Bone marrow concentrate
· Direct grafting of stem cells
The use of BMC and PRP injections have been effective in addressing failed healing or delayed healing fractures. Other recent developments also show BMC and PRP to be effective in rib and mandibular fractures (6). Meanwhile, through the direct grafting of tissue-specific stem cells, MSCs that have matured into the desired tissue type can be integrated into the target tissue (5). Let’s take a quick look at each of these methods.
Platelet-rich plasma
PRP contains a high concentration of platelets and various biologic substances such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and many others. As the cells are derived from the patient the potential for adverse reactions and infection is very low. PRP is not made up of stem cells, but the use of PRP has been found to stimulate MSC proliferation. Thus, PRP is a vital component of stem cell-based therapy in sports-related injuries (7).
A study published in 2012 showed that the local application of PRP in the repair of rotator cuff injury in patients reduced the pain after surgery. In addition, long-term results showed that PRP aided in the healing of rotator cuff injury in patients (8).
Bone marrow concentrate
Bone marrow concentrate (BMC) is another tool that is used for sports-related bone injuries and other lesions. BMC is a rich mixture of MSCs, different bioactive molecules, white blood cells, and platelets. Just like PRP, BMC is also harvested from the patient. This reduces the risk of infection and immune reactions. BMC is used to deliver stem cells to damaged bone, thus initiating repair and healing.
A clinical study done in 2016 showed that treatment of discogenic back pain with BMC injections provided relief of pain and disability improvement. BMC was delivered via disc injection to 26 patients, which showed improvement over the span of 2 years. This will not only benefit athletes with back injuries, but also the general public who could be chronically experiencing back pain (9). Another study published in 2015 reported that the use of BMC for open Achilles tendon repair resulted to excellent outcomes, characterized by early mobilization and zero re-ruptures (10).
Direct grafting of stem cells
Emerging biotech research studies have used the direct grafting of stem cells to focus on the production of tissue engineered bone bioscaffolds. These bioscaffolds are meant to function as a porous and permeable solid structure for stem cell attachment, growth, and migration. Such scaffold material would make it easier for stem cells to adhere to the injured tissue and promote growth of new cells (5). Most of the current studies on the use of stem cells on grafts to repair bone and muscle injuries are still experimental. No clinical trials have been reported so far.
How much does stem therapy cost?
The cost of stem cell therapies depends largely on the specific type of stem cells and tissues involved and the extent of injury. In the US, stem cell therapy for knee injuries range from $3000 to $5000 but the most expensive ones can reach up to $50,000. The same type of treatment costs as low as $2000 in Mexico and in Asian countries such as Thailand.
References
1. Stem cells and the evolving notion of cellular identity. Daley, G. 1680, 2015, Vol. 370.
2. Adult stem cells: hopes and hypes of regenerative medicine. Dulak, J., et al. 3, 2015, Vol. 62.
3. Browne, C., Chung, T. and Atkinson, K. The Biology of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Health and Disease and Its Relevance to MSC-Based Cell Delivery Therapies. [book auth.] L. Chase and M. Vemuri. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy. New York : Humana Press, 2013.
4. American Physical Therapy Association. Sports and Recreation-Related Injuries Top 8.6 Million Annually. APTA. [Online] January 4, 2017. https://www.apta.org/PTinMotion/News/2017/1/4/SportsInjuries/.
5. Young, M. and Doran, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapies for Bone and Tendon Conditions. [book auth.] L. Chase and M. Vemuri. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy. New York : Humana Press, 2013.
6. Siddiqui, I., Mazzola, T. and Shiple, B. Techniques for Performing Regenerative Procedures for Orthopedic Conditions. [book auth.] G. Malanga and V. Ibrahim. Regenerative Treatments in Sports and Orthopedic Medicine. New York : Demos Medical Publishing, 2018.
IS HGH AN EFFECTIVE ANTI-AGING DRUG?
Growth Hormone (GH) has been shown to offset many of the side effects of aging. Supplementation can reduce body fat, increase lean muscle, improve skin elasticity, energy and sex drive. Many claim GH is a »fountain of youth«. However several studies point to a significant potential downside - increased GH levels may reduce lifespan. In this article we will discuss the latest findings and the pros and cons of GH supplementation for anti-aging.
Growth Hormone (GH) has been shown to offset many of the side effects of aging. Supplementation can reduce body fat, increase lean muscle, improve skin elasticity, energy and sex drive. Many claim GH is a “fountain of youth”. However several studies point to a significant potential downside - increased GH levels may reduce lifespan. In this article we will discuss the latest findings and the pros and cons of GH supplementation for anti-aging.
WHAT IS A HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE?
HGH or GH is a hormone produced by the pea-sized pituitary gland that is located at the base of our brains. In the early stages of our lives it fuels growth, it also helps maintain tissues and organs throughout life.
WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF GROWTH HORMONE?
GH stimulates body growth by stimulating the liver and other tissues to secrete IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor). IGF-1 is anabolic - it increases lean muscle mass and reduces fat tissue simultaneously. It also promotes neurogenesis which is the growth of new brain cells and has neuroprotective properties – it prevents brain cells from dying.
However, as we age there is a natural slowdown in GH production and consequently IGF-1. This can lead to muscle wasting, loss in bone density, reduced skin elasticity, increased fat retention, loss of immune function and cognitive decline – many of the signs we associate with aging.
Many people supplement synthetic GH to prevent some of the side effects of aging. HGH promoties muscle, bone growth and also slows down apoptosis. Apoptosis is a programmed cell death that protects against the spreading of infectious diseases and cancer, but it can also lead to the death of healthy cells as we get older. GH also promotes new nerve growth in the brain which can lead to better cognitive performance and wellbeing (1) (2).
WHAT EFFFECT DOES IT HAVE ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM?
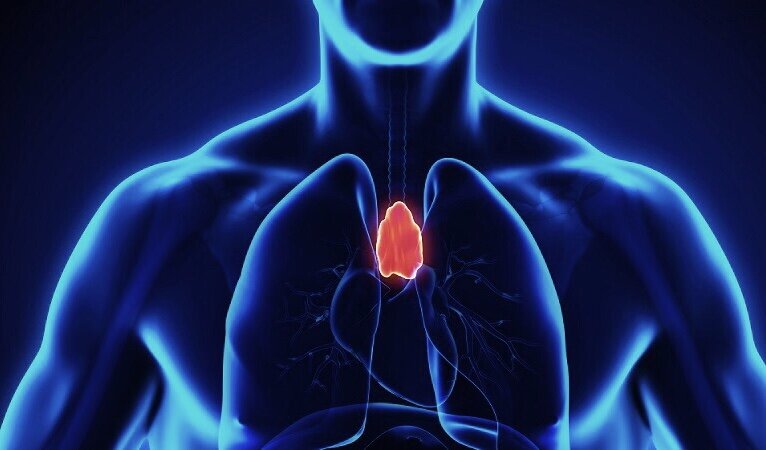
Our immune systems deterioate with age. One of the organs responsible for our immune system to function properly is thymus – this is the primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within lymphoid organs T-cells mature. T-cells are type of white blood cells that are essential part of our immune system. They determine the specificity of immune response to foreign substances in the body or in other words – antigens.
The thymus is fully developed by the time we are 10 years old but then it starts shrinking. This gradual shrinking is related to the decline in our immune systems as we get older.
So called thymic involution (the shrinking of the thymus with age) leads to growing mortality risk, decrease in tissue mass and depletion of critical immune cell populations. That is linked to age-related increases in cancer incidence, infectious diseases, autoimmune conditions, generalized inflammation and atherosclerosis (3).
Supplementation with GH has been shown to help rejuvinate the Thymus and therefore boost our immune systems.
THREE-DRUG COMBINATION TO BOOST THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
From 2015-2017 a human clinical trial was conducted in attempt to reverse various aspects of human aging. It was called TRIIM (Thymus Regeneration, Immunorestoration, Insulin Mitigation). In this trial they used growth hormone to reverse biological aging of the immune system in a population of 51 to 65 year old healthy men.
GH is known to increase blood sugar levels so they used combined GH with DHEA and metformin to keep blood sugar levels in check. Metformin is used to treat people with type 2 diabetes and has been proposed as a candidate for slowing aging in humans before. All of the mentioned drugs (GH, DHEA, metformin) have been linked to slowing the aging process in the laboratory (4).
During the trial the composition of thymus was checked and blood samples were taken to analyze immune cell counts. The trial's results were impressive, the patients Thymus' appeared to regenerate, fat tissue was replaced with regenerated, healthy tissue. Not only that, the parcipants' biological age was 1.5 years lower than when they first entered the trial! The sample size in this study was small but the results were very consistent
What is interesting is that this study showed that supplementing with GH for a relatively short time period led to a rejuvination of the thymus. Other studies have demonstrated similar results, short term supplementation such as 6 months can lead to significant changes in our organs, winding back the body clock by years (5).
SO WHAT IS THE DOWNSIDE?
While GH may help you to feel and look younger, increased levels of GH (or more specifically IGF-1) has been linked to shorter lifespan. This has led to a great deal of confusion in the anti-aging community, is GH a fountain of youth, or a potential accelerant of the aging process?
In experiments in mice, worms and flies the subjects with lower levels of GH lived longer. Mice with GH and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) deficiencies lived 50 % longer than mice of the same species with no deficiencies. It appears GH or at least IGF-1 promotes growth but also depresses life span across many species (6). In humans decreased IGF-1 is in fact correlated with the longevity of centenarians (people who has reached the age of 100 years).
Elevated levels of circulating IGF-1 might decrease lifespan because IGF-1 causes increased cell proliferation which can raise our suceptibility to diseases such as cancer (7). Too much of human growth hormone can also cause arthritis, diabetes and even heart failure.
Reduced growth hormone and IGF-1 may also increase lifespan by increasing the expresion of genes that are involved in stress resistance and DNA repair.
However, we should be wary, the reduction of IGF-1 expression levels can come at an expensive cost especially when it comes to muscle and brain maintenance and repair. Results from various studies have been very inconsistent (8).
IS IT A TRADE OFF?
Ecologists and other evolutionary biologists have pointed out dozens of trade-offs in natural populations. Perhaps individuals that reproduce (or reproduce more) have a corresponding decrease in some fitness trait such as longevity (9). Evolution may be forced to accept costly tradeoff later in life in exchange for better chances for early individual reproductive success.
IGF-1 is good example of an evolutionary trade off. IGF-1 stimulates rapid growth (tissues and organs growth) and development in early stages of our lives but it can also have some negative long-term effects such as cancer and can increase mortality.
This theory works very well with the counterintuitive findings that most of the »longevity genes« discovered in various organisms are either loss-of-function mutations or mutations that reduced the level of gene expression (8).
The evidence to support this theory is still limited. There is a lot of IGF-1 early in our lives but the effects are not as harmful. Later in life IGF-1 is at very low levels so the correlation between higher levels of IGF-1 in our teens and risk of cancer and other diseases in our older years is very hard to explain.
how can we balance the benefits, while minimizing the risks?
FIRST TRY TO BOOST GH LEVELS NATURALLY
Some scientists claim enhancing GH and IGF the natural way may maximize the benefits without the costs. There are natural and effective ways we can increase natural growth hormone levels:
Strenuous exercise has been shown to increase growth hormone levels
but it is important to mention that we can get acclimated to exercise over
time which will lead to less hormone secretion from glands.
Intense heat stress induces a massive rise in GH - 30 minute sauna
therapy has been shown to cause a rapid boost in growth hormone levels.
A research study from 2007 found that group with a 30 minute
continuous sauna session showed higher elevations in hGH levels (10).
Eat a healthy diet, rich in healthy fats and low in sugar.
Get plenty of sleep.
DON'T GO CRAZY
If you choose to supplement with GH, make sure you see a doctor and get your blood tested first. Supplementation with exogenous GH is only recommended for people who are unable to boost their GH to healthy levels using the natural methods described above.
Supplementation is usually only considered for people older than 40, this is when the drop in GH becomes more noticable. If supplementing make sure the dose you take doesn't take your GH levels higher than that of a health 30 year old.
Only supplement for short periods of time (not more than 3 months) and take regular breaks. Supplementing for 3 months once per year should be more than enough to restore the thymus to healthy function. Not taking GH for extended periods will help to reduce the potential negative impact on longevity.
CONCLUSION
Growth hormone supplementation provides many physical and psychological benefits however the correlation between higher GH levels and shorter lifespans is worrying - therefore moderation is advised. Further research with larger and more diverse populations are needed before we will fully understand how to maximise the benefits and minimize the risks. In the meantime try boosting your GH levels naturally, through high intensity training, sauna, a healthy diet and making sure you get plenty of sleep. If you decide to supplement do so only under the supervision of a doctor and not for more than 3 months a year.
REFERENCES
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2682398/
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6305861/
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6276058/
4. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/acel.13028
6. https://academic.oup.com/biomedgerontology/article/67A/6/652/583809
7. Longo, V. D. and L. Fontana. 2010. Caloric restriction and cancer prevention: metabolic and molecular mechanisms. Trends Phamacol. Sci. 31:89-98.
8. https://wjmh.org/DOIx.php?id=10.5534/wjmh.180018
9. Leroi, A. M., A. Bartke, G. D. Benedictis, C. Franceschi, A. Gartner, E. Gonos, M. E. Feder, T. Kivisild, S. Lee, N. Kartal-Ozer, Schumacher, M., Sikora, E., Slagboom, E., Tatar, M., Yashin, A. I., Vijg, J, and B. Zwaan. 2005. What evidence is there for the existence of individuals genes with antagonistic pleiotropic effects ? Mech. Age. Dev. 126:421-429
10. https://journals.indexcopernicus.com/search/article?icid=890538
What is intermittent fasting and what are the benefits?
Intermittent fasting, refers to a diet that involves avoiding food intake, for a period of time, on a regular basis. Intermittent fasting delivers many benefits beyond just weight-loss, it may even help to extend lifespan. In this article we explore what intermittent fasting is, what benefits it can deliver and various methods of practicing this diet.
Intermittent fasting, refers to a diet that involves avoiding food intake, for a period of time, on a regular basis. Intermittent fasting delivers many benefits beyond just weight-loss, it may even help to extend lifespan. In this article we explore what intermittent fasting is, what benefits it can deliver and various methods of practicing this diet.
What is intermittent fasting?
Intermittent fasting is a special diet in which people have to restrict how much or when they eat food in a given period of time. It involves eating food only during a specific number of hours in a day or week.
Intermittent fasting differs from other diets in that it does not tell you what you can or can’t eat, nor how much to eat. During the feeding times you can eat whatever you want, and as much as you want!
There are various methods of intermittent fasting, some lasting hours and some lasting several days, we will go into more detail on the different methods of fasting later in this article.
Typically, during the period of fasting you may not eat any food, however there are exceptions on some longer fasting programs you may be allowed a small amount of calories. During the fasting period you are allowed to drink water, unsweetened tea and coffee, and other low-calorie beverages.
What are the benefits of intermittent fasting?
Promotes longevity
Animal studies have shown that intermittent fasting can significantly extend lifespan. The results are striking, in one study rats who fasted every other day lived 83% longer on average than the control group (1).
While the effect on longevity hasn’t been proven in humans, intermittent fasting has been shown to deliver a range of benefits in humans which should contribute to increased lifespan, these are outlined below.
Promotes weight loss
Obesity is one of the common precursors to several diseases including heart attacks, high cholesterol, stroke, hypertension, and diabetes. These disorders are known to reduce the lifespan of a person and also affect their quality of life.
Intermittent fasting can promote weight loss by triggering the use of fats stored in the body (2).
Intermittent fasting involves eating fewer meals, which reduces the calorie intake of a person. Unless the person compensates for the reduced number of meals by overeating during the phase of food intake (typically you won’t), the overall calorie consumption of a person stands reduced.
Intermittent fasting also causes reduced insulin production, increased growth hormone secretion (up to 5x normal amounts), and increased norepinephrine levels all of which support the breakdown of fats to be used as energy (3) (4).
Fasting is a quick way to lose weight
May help prevent cancer
Fasting slows down the rate of cell growth, and stimulates autophagy, the body’s clean up mode. Both of these effects may help to reduce the growth of cancers, or even eliminate small tumors and pre-cancerous cells. Conclusive human studies are still needed but the results in animals appear promising.
In one study a group of rats were infected with tumors, 50% of those on calorie restriction survived 10 days later, whereas only 13% of those with normal diets survived (5).
In addition, fasting during chemotherapy treatment seems to reduce the side effects of chemotherapy. This works because chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing cells. During fasting cell division slows down, this slowing effect is far more pronounced in regular tissues than in cancer cells. Thus the chemotherapy is able to better target cancer cells while affecting fewer healthy cells (6).
Improves organ and brain health
Intermittent fasting can improve the health of vital organs including the brain, heart, liver, and kidneys, thereby improving longevity. For example; research studies have revealed that intermittent fasting can improve the risk factors for heart attacks such as hypertension, inflammatory markers, cholesterol and triglycerides levels, and blood sugar levels (7).
It can also slow down the degenerative changes in the brain and improve cognitive functions such as memory, attention span, and problem-solving skills. It may reduce the risk of degenerative brain disorders like Alzheimer's disease, and dementia and thus, improve longevity (8).
Fasting can help protect our brains from degenerative diseases like dementia
How else does it benefit longevity, at a cellular level?
Improved cellular clean up processes
Our cells incur a huge amount of DNA damage on a daily basis. This is caused by environmental factors such as solar radiation and pollution, by-products from our metabolism such as free radicals, and the DNA replication itself is prone to error.
Fortunately, our bodies can repair damaged DNA. One method of DNA repair is via the sirtuin proteins. Sirtuins are a family of proteins that assist in DNA repair. They are activated when the body senses it is in a stressed state (e.g. fasting). Activating the sirtuins accelerates the DNA repair processes in our bodies.
Fasting also stimulates a cellular detoxification processes known as autophagy (9). Autophagy is the body's way of cleaning out cellular trash to restore the health and functioning of cells. This cellular trash if left uncleared can lead to inflammation and even cancer.
Every day our DNA incurs millions of DNA strand breaks, which need to be repaired
Improved mitochondrial functions
A research study conducted by Harvard researchers has shown that intermittent fasting could increase lifespan by slowing down degenerative changes in the body and delaying the effects of aging. It is believed to work by improving general health by modifying the activities of the mitochondrial network inside the body cells and tissues (10).
Mitochondria work like small power plants for our cells. Mitochondria also play a key role in the aging of the cells. The studies have shown that changing the shape of mitochondrial networks can enhance the power generating abilities of the cells and thereby improve their longevity and lifespan.
More importantly, it also illustrates that fasting could manipulate these mitochondrial networks and thus, maintain their "youthful" state (11).
Mitochondria are the power factories of our cells
Reduced oxidative stress and inflammation
Oxidative stress and inflammation in the cells can speed up the aging process.
Oxidative stress occurs due to the damage caused by unstable molecules known as free radicals. Free radicals have the ability to react with and damage other molecules such as proteins and DNA. This can trigger degenerative and cancerous changes in healthy organs. Similarly inflammation in the body can cause damage to nearby cells and DNA.
Several studies have shown that intermittent fasting could enhance the body's resistance to free radical damage or oxidative stress and reduce inflammation to slow down aging. It can also reduce the risk of cancer by protecting healthy cells against toxins and carcinogenic agents like free radicals (12).
What method of intermittent fasting seems to be the most effective?
There are several different forms of intermittent fasting, the most common approaches are described below. Ultimately, the best method of fasting is the one which works for you. Choose something you can stick to and incorporate in your routines.
Shorter fasts
Shorter fasts last for less than 24 hours. Shorter fasts are more suitable for people who are new to fasting and are not used to avoiding food intake for prolonged hours. Shorter fasts still deliver a range of benefits and can be easier to incorporate into your weekly habits.
There are two common approaches, the 16:8 and the 20:4.
In 16:8 intermittent fasting, the person should fast every day for 16 hours continuously. Sometimes, it is also called the 8-hour eating ‘window’ method. All meals should be consumed within the 8-hour time period. The 8-hour time period needs to be continuous and cannot be broken down into two or more phases.
For the rest of the 16 hours of each day you should not consume any calories. This method can be followed safely every day.
An example of 16:8 is eating all your food between 11:00 am and 7:00 pm. This would require you to skip breakfast and have an early dinner. You can eat 2 or 3 meals during the 8-hour period. You can also choose any continuous time period of 8 hours to eat depending on your routine or personal preferences.
20:4 is another form of short fasting method that involves a 4-hour window for eating and a 20-hour window for fasting. You can choose a continuous time period of 4 hours such as between 1:00 pm and 5:00 pm every day and avoid food intake for the remaining 20 hours. This would generally involve eating 1 meal or 2 smaller meals within the 4-hour period.
Shorter fasts need to be done more frequently in order to derive the expected health benefits.
24-hour fasts
A longer fast of 24 hours can be adopted by those who feel they have the capacity to go without food for a longer duration. We suggest you try a couple of shorter fasts first before working your way up to a 24-hour fast.
The 24-hour intermittent fasting involves avoiding food intake from lunch to lunch or dinner to dinner. For example; you can eat dinner on the first day, , skip breakfast and lunch the next day, then eat dinner. This form of intermittent fasting is usually done 1 to 3 times per week.
The 5:2 intermittent fasting approach is a popular form of the 24 hour fast. The 5:2 approach involves fasting for 24 hours 2 times per week, on the other 5 days you can eat normally.
Alternate-day fasting is another common approach to the 24 hour fast whereby a person fasts for 24 hours every second day. During the other days they can eat normally.
Extended fasting
This form of intermittent fasting lasts for more than 24 hours. Extended fasting is recommended only for people who have some experience with fasting and are already comfortable fasting for 24 hours. Anyone considering extended fasting should consult their doctor first to ensure they would not be at any risk while fasting.
Extended fasting involves avoiding food intake for 2 to 14 days. Fasting for more than 14 days is not advisable as it can increase the risk of refeeding syndrome, which occurs due to the dangerous shift in minerals and fluids once food is re-introduced after a long period of fasting.
It is advisable to use multivitamin supplements during extended fasting to avoid nutritional deficiencies.
Can I consume some calories when fasting?
If you find it difficult to go completely without food for 24 hours you can still achieve many of the benefits of fasting if you consume only a small number of calories during the fasting period.
This approach won’t deliver such extreme changes as fasting completely however incorporating some calories can make fasting more sustainable in the long term for many people, therefore leading to better long term results.
If you do consume calories it is important not to consume more than 800 calories in the fasting period. 800 calories should be sufficient to help avoid food cravings and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia or low blood sugar levels. The calories can be consumed as a single meal or spread throughout the day.
If you eat on fasting days, try to stick to low calorie foods which are high in fiber
How often do you need to fast?
It is only when intermittent fasting is adopted as a dietary habit over several weeks or months that a you will see real long term results, and derive benefits such as improved longevity.
If you choose the shorter fasting approach, this should be done at least 3-5 times per week. 24-hour fasts can be done 1-3 times a week. The frequency of longer fasts depends upon duration. A 48 hour fast could be done once per week but a 4 day fast should not be done more frequently than once per month.
Intermittent fasting is easier for most people to maintain than a regular diet. Start with shorter fasts and work your way up from there. Find an approach that works for you, one which you can incorporate within your routine, and stick with it. If you do you will see results.
REFERENCES
https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(17)30612-5
http://www.ncl.ac.uk/press/news/2016/02/mitochondriashowntotriggercellageing/
Cycloastragenol – a revolutionary anti-aging drug or a cancer risk?
Cycloastragenol (CAG) has been heralded by some as a miracle anti-aging agent. Early studies appear promising, showing it has the ability to increase telomere length, however there is a still a lack of quality peer-reviewed research. In addition, there is some concern that taking CAG may increase the risk of certain cancers. In this article we will discuss what CAG is, how it works and the latest findings as to its efficacy and risks.
Cycloastragenol (CAG) has been heralded by some as a miracle anti-aging agent. Early studies appear promising, showing it has the ability to increase telomere length, however there is a still a lack of quality peer-reviewed research. In addition, there is some concern that taking CAG may increase the risk of certain cancers. In this article we will discuss what CAG is, how it works and the latest findings as to its efficacy and risks.
What is Cycloastragenol?
CAG is a molecule derived from Astragalus membranaceus herb. The Astragalus herb has been used in Chinese medicine for centuries. The Chinese claimed that Astragalus can prolong life and it has been used it to treat fatigue, allergies, colds, heart disease and diabetes.
CAG is one of the active ingredients in Astragalus.
Astragalus used in Chinese medicine is one of the primary sources of CAG.
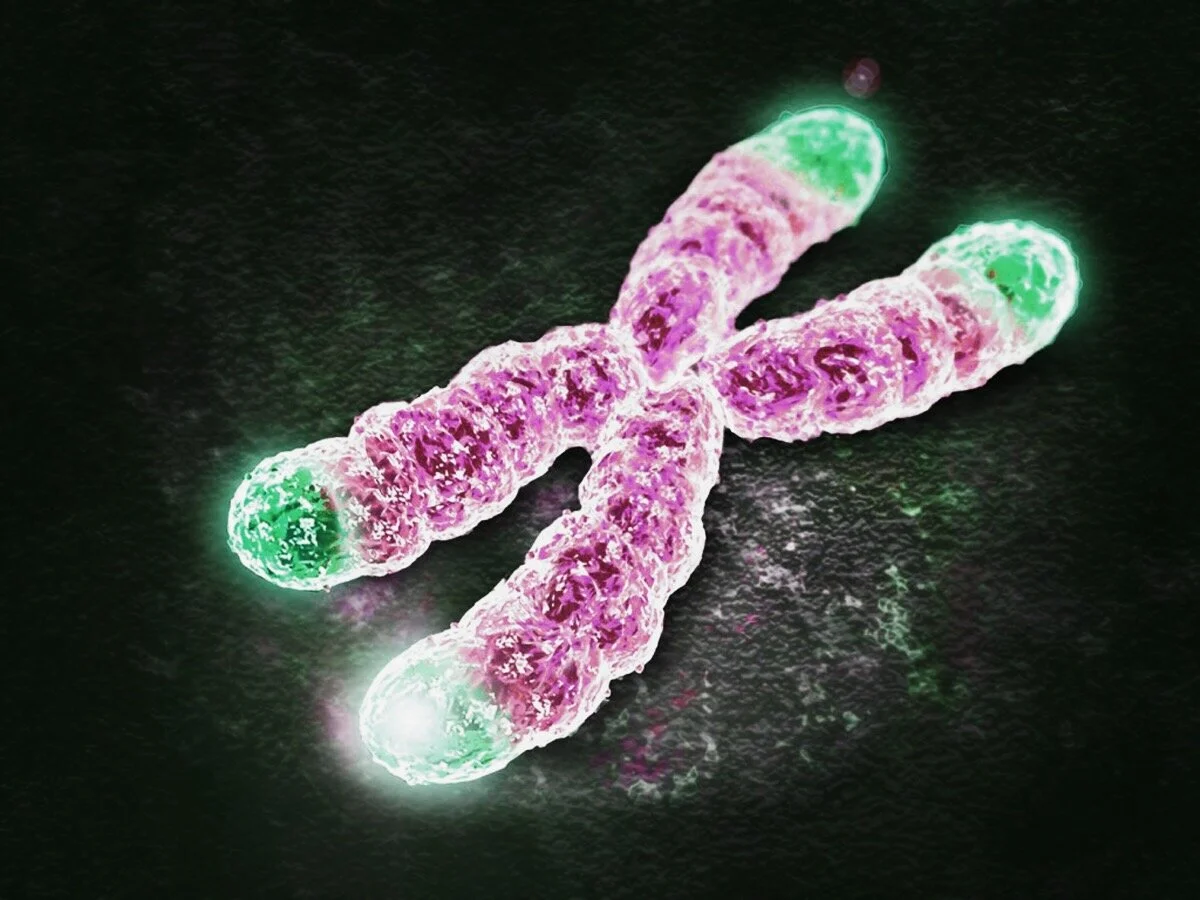
What are telomeres?
Telomeres are sequences of repeated genetic code located on the end of DNA strands.
Each time a cell divides, our DNA is copied from the old cell to the new cell. As the DNA is copied a small part of the DNA is lost from the end of the DNA strand. The telomere is the sacrificial end of the DNA strand. Each time our cells divide a part of the telomere is lost and the telomere becomes shorter.
When the telomere ends get too short, the DNA can no longer be copied and the cell refuses to divide any further. The average length of telomeres is a good indicator of biological age in most organisms (shorter = older).
Our cells divide for many reasons one of which is to replace damaged and dead cells. Our skin cells are constantly dividing as we lose approximately 30,000 to 40,000 skin cells every minute!
The number of times each cell can divide is limited. The average cell will divide between 30 to 90 times before cell death. Once this limit is reached, the cell will no longer divide, thus in theory the ability for that tissue to grow or heal would be greatly reduced, potentially leading to typical signs of aging.
Fortunately, cells have the ability to secrete an enzyme called telomerase, which can add telomeres back to the ends of the DNA. When telomerase causes telomers to become longer, it leads to the turning back of the age-clock (1).
Telomeres are the “protective caps” on the end of DNA
How does CAG work?
CAG is well absorbed by the body as it can pass through and be absorbed by the intestine. It later undergoes further metabolism in the liver.
Extensive pharmacological properties have been attributed to CAG. It activates the telomerase enzyme and consequently may causes telomere elongation, it produces anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative actions and is also reported to support healthy lipid metabolism (2).
CAG’s ability to induce telomere elongation is one of the main reasons CAG has generated so much excitement in the anti-aging community. In mice premature aging has been reversed through increased telomerase production (3).
What are the benefits of CAG?
The elongation of telomeres would allow each cell to last longer and also support the body's ability to produce new cells through more cell divisions (4). This would enable the body to replace dead and damaged cells for longer, potentially reducing aging.
Clinical research studies have demonstrated that CAG can activate telomerase in humans (5). These properties of CAG led to the belief that CAG could be used as an antiaging agent.
Later research studies were focused primarily on assessing whether CAG could actually defy the signs of aging. In various studies CAG has been shown to reduce fine lines and wrinkles, boost immunity and improve vision (6), (7), (8).
While these studies demonstrate CAG may be beneficial in increasing healthspan, no studies have yet conclusively demonstrated CAG’s ability to extend lifespan in humans.
Is CAG safe?
There is some concern that CAG may increase the risk of cancer. Critically short telomeres lead to apoptosis (cell death), in the case of cancer this would be a good thing! By preventing shortening of telomeres, the bodies ability to induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is affected. Apoptosis is the body’s natural defense mechanism that can help to kill the abnormal cancer cells selectively (9).
In fact, telomeres are already elongated by telomerase enzyme in nearly 80% of tumors, that is one of the reasons they are so hard to kill (10). Elongation of telomeres due to telomerase could in theory prevent the destruction of cancer cells thereby contributing to tumor growth.
Apoptosis, is the death of cells which is a normal and natural part of development
A lawsuit has been filed by an employee against the manufactures of a well-known CAG product.
The employee, Egan, was hired by Patton in May 2011 to help expand the reach of Telomerase Activation Sciences in foreign markets. Telomerase Activation Sciences sells a supplement called TA-65, which is claimed to elongate short telomeres.
Egan was asked to take these pills twice a day. However, later, on 14 September, he was diagnosed with prostate cancer, which, according to the lawsuit filed by Egan, could be due to TA-65.
However, research studies have not been able to establish any cancer risk associated with the use of CAG. Laboratory research studies in animals have shown that CAG does not induce any genotoxic or toxic effect. In a research study, the administration of CAG to rats for 3 months did not show any rise in the incidence of cancer (11).
This indicates that while physiological processes involved in cell division do suggest that CAG could cause cancer, there has been no clinical evidence to prove this claim.
Conclusion
CAG looks like a promising anti-aging compound. While it has not been proven to increase lifespan yet it has been shown to reduce various age associated biomarkers. In addition it has been shown to reduce the signs of aging such as fine lines and wrinkles. It may also reduce the risk of degenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, Parkinson’s, retinopathies, and cataracts.
However, it is advisable to not ignore the potential risk of cancer. Careful evaluation of the safety of CAG through further long-term scientific studies is required. Anyone with a personal or family history of cancer may be advised to avoid CAG until more long-term safety studies have been conducted.
References: