RECENT
Everything You Need to Know About Heart Rate Variability
Heart Rate Variability – or simply HRV – is said to be an indicator which can be used to monitor overall health, biological age, aerobic fitness and levels of stress. HRV has recently become a popular metric among biohackers and fitness fanatics, especially as technological advances now make it possible to measure at home.
What is Heart Rate Variability?
Heart Rate Variability – or simply HRV – is said to be an indicator which can be used to monitor overall health, biological age, aerobic fitness and levels of stress. HRV has recently become a popular metric among biohackers and fitness fanatics, especially as technological advances now make it possible to measure at home.
HRV is the difference in timing between each heartbeat interval. The variation between heartbeats is controlled by a particular part of the nervous system referred to as the Autonomic Nervous System or ANS.
What is the ANS?
The ANS controls most of our internal organ functions, such as the heart, stomach and intestines. The ANS works whether we want it to or not, that is why you don’t have to consciously decide for your stomach to digest your food.
The ANS is a critical part of our breathing, blood pressure and digestion processes. The ANS helps keep the bodies internal environment (temperature, blood sugar, oxygen etc.) in balance.
The ANS is divided into two sub-components, namely the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system. In layman’s terms, these are known as the relaxation response and the fight-or-flight reaction (1).
The parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic system, or relaxation response, helps with the day to day tasks such as digestion, slowing the heart rate and decreasing blood pressure.
The sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic system, or fight and flight response, prepares the body for energy output and protects it from injury. It shuts down the gut, speeds up heart rate, increases blood pressure and increases blood sugar for energy consumption.
The sympathetic system is associated with the fight or flight response.
The brain responds to stimuli in our environment and subconsciously decides whether the body should be relaxed or in a fight or flight state. The brain sends signals from the hypothalamus to the ANS to trigger these responses in the rest of the body.
A poor night’s sleep, a stressful day at work or an argument with a loved one are some examples of negative stimuli which can trigger the fight or flight response. The body is usually capable of handling negative stimuli on a day to day basis. However, if one constantly experiences too much stress and unhealthy relationships with others, this may result in an excessive fight-or-flight response.
What Does Your Heart Rate Variability Tell You?
For a regular healthy person, the heart rate variability should increase whenever they engage in relaxing activities. If that person is doing yoga, lying in bed or simply resting, their parasympathetic nervous system is in control and their HRV is high. On the contrary when stressed, the sympathetic nervous system takes control, this results in a lower HRV (2).
HRV levels naturally change in response to your day-to-day encounters and interactions. However, chronic stress can result in the sympathetic nervous system or fight or flight response being in constant control. In healthy individuals the heart is able to quickly switch between sympathetic and parasympathetic states, resulting in a high HRV, whereas people with cardiac problems, or experiencing chronic stress may show a low HRV.
Research has shown a relationship between low HRV and depression, anxiety, cardiovascular disease and an increased risk of death (3).
A low HRV could predict an early death!
How can I use HRV?
Stress tracking
Measuring HRV over a few minutes at the same time each day (e.g. upon waking) can provide you with a useful metric for monitoring stress levels. Knowing when your HRV is low can help you incorporate healthy habits into your day when they are most needed.
Activities such as mindfulness, meditation, sleep, and physical activity can all help increase HRV.
Prevent over-training
Elite athletes and trainers monitor heart rate in conjunction with HRV to conduct various tests to determine when the body is in need of rest or conversely when it is recovered and ready to train again. Conducting such tests reduces the risk of overtraining.
Many of the HRV monitoring devices and apps have such tests built in. One example is the Orthostatic Test from Polar (4).
What is a good score?
Generally a higher HRV score is an indicator of good health however it is not easy to define what constitutes a “good” score. HRV scores will change significantly for individuals depending on time of day, their position when the reading was taken and their activity levels. There are also a number of different ways to measure HRV and as yet there is no standardized approach (5).
It is therefore important to only compare HRV scores taken at similar times under similar circumstances and on the same device. For example upon waking, in a seated position and using a polar chest strap with the Welltory app.
The best way to judge your HRV is to monitor it over time. It is worth taking note of the average score when you are in periods of low stress, such as a holiday, and then comparing the readings on days after intense exercise or when you are experiencing lots of stress at work. There are a number of apps (mentioned below) which allow you to easily monitor this.
For those determined to know how they stack up against the general population we have included some stats below. These values are based upon the rMSSD method (6,7,8,9):
Young, highly trained individuals 70 - 120
Young sedentary individuals 30 - 50
In patients with chronic heart failure in the 20s
Methods of measuring Heart Rate Variability
Most devices employ one of two approaches to monitor HRV, an ECG or PPG.
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is the most accurate way to detect HRV. An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart. This method requires electrodes to be placed directly on the chest. The electrodes require secure contact with the skin to work effectively.
PPG
Photoplethysmography (PPG) differs from an ECG in that instead of measuring the electrical activity it illuminates the skin with a small light and then measures changes in light absorption. The skins light absorption changes in response to blood pressure and blood flow, thus this can be used to monitor HRV.
While PPG can produce good results it can easily be disrupted, any motion during measurement or light pollution can result in an incorrect reading.
Recommended devices for HRV monitoring
Gone are the days when you have to be sent to the hospital just to get your HRV checked. There are now many compact and convenient devices which allow you to check you HRV whenever you want.
A chest strap which utilizes ECG technology will provide the most accurate results. Some fitness watches also claim to produce reliable HRV measures but results vary, most of these watches use PPG technology.
Recently a number of mobile phone apps have been released allowing users to measure HRV using their phone. The apps access the phones camera which uses PPG technology to measure HRV. Some companies claim these measures are accurate however there is still a lack of independent studies. When we tested these apps using both PPG via the camera and ECG using a chest strap we found the results varied significantly.
For the average user curious about HRV and interested in taking the occasional HRV reading we recommend downloading one of the apps below and using your phones camera to take a PPV reading. For the more serious enthusiast interested in monitoring HRV on a daily basis or during your exercise workout, we suggest investing in a chest strap.
Recommended mobile apps
Here are just some of the best apps when it comes to measuring and recording HRV.
Welltory
This is one of the most user-friendly HRV-measuring apps for both iPhone and Android users.
Welltory allows users to measure their HRV using the phones camera, the camera uses PPG technology to measure HRV. Welltory can also be used with a variety of chest straps and fitness watches for a more accurate measure of HRV.
Welltory also connects to a very wide range of other fitness trackers and apps. Welltory has a user friendly interface and can break down your HRV results easily and divide them into comprehensible categories. These categories include performance, energy and stress levels.
The basic version is available free however a fee is required to access to access premium features.
HRV4Training
HRV4Training is another app that you can download whether you’re on an iPhone or Android device. This app also allows you to use your phones camera to obtain a PPG reading of your HRV. For a more accurate reading the app can also be used with a chest strap to obtain an ECG reading.
It’s designed to track your metrics in 30-days and then provide training suggestions on how you can do better. Unfortunately there is no free version and the basic version starts at $9.99.
Elite HRV
Elite HRV is another free app available to both Android and iPhone devices. The main drawback is that it requires an external heart rate monitor, it will not allow you to use your phones camera to generate a PPV reading. We also found the design is not as user friendly as Welltory or HRV4Training.
The app is free for both operating systems, but to access the full feature set you need to pay $4.99.
Recommended devices
The apps Welltory and HRV4Training will allow you to take a PPG HRV reading using your phones camera. A PPG HRV reading can also be obtained using most high end fitness watches (Garmin, Polar) and even the Apple watch. For the average person a PPG reading is sufficient.
For the serious enthusiast who wants a more accurate ECG reading a chest strap is required. Below are some suggestions.
Polar H7 Bluetooth Heart Rate Sensor
Polar is an established company, well-known for its heart rate and exercise-assistive products. Their H7 Bluetooth Heart Rate Sensor can be comfortably worn on the chest and is available in two sizes. It has up to 200 hours of battery life.
The H7 uses ECG technology for a more accurate reading and is one of the more affordable HRV monitoring devices available.
Polar H10 Bluetooth Heart Rate Sensor
This is the newer model from Polar, some of the upgrades include a doubling of the battery life to 400 hours. And this model is waterproof,
so suitable for swimmers.
Garmin Premium Heart Rate Monitor
This heart rate monitoring device from Garmin measures your HRV while keeping you comfortable with its soft strap. It’s also a waterproof device so you can use it while swimming.
It can easily transmit data to any other Garmin fitness tracker or your preferred iOS or Android app.
Drugs and supplements for sexual performance
We examine various drugs and supplements which have been shown to increase libido, in men and women. Including Cabergoline, Bromocriptine, Mucuna Pruriens, Tribulus Terrestis, D-aspartic acid and L-Citrulline.
Whether you have low libido or are just looking to spice things up in the bedroom, this article may be for you. We will examine various drugs and supplements which have been shown to increase libido, in men and women.
Low libido affects around 15% of men and 32% of women (1). The leading causes of libido suppression include stress, anxiety, depression, diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, and cholesterol. In addition, certain sex hormones decline with age, especially in men.
There are many lifestyle changes which can have a positive impact on sex drive, and these should be explored before considering drugs or supplements. Behaviors such as consuming a healthy balanced diet, exercising regularly, maintaining healthy levels of stress and anxiety and getting at least 7 hours of sleep a night can all can help with libido. However for those who have tried such changes or are still looking for an additional boost, there are a number of drugs and supplements which can be effective.
Most of the drugs and supplements which impact libido operate via one of 3 mechanisms of action; i) via dopamine and / or prolactin, ii) via androgenic hormones, or iii) through vasodilation.
The Dopamine / Prolactin connection
Dopamine and prolactin are closely linked to sex drive. It is theorized that dopamine increases sexual desire while prolactin reduces it, the link between dopamine and sex drive has been well established in men, but is less clear in women (2).
Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter, involved in many pathways in the brain. Dopamine is associated with motivation and concentration. Too much or too little dopamine can be detrimental, low dopamine can lead to Parkinson’s disease while abnormally high levels of dopamine have been linked to schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders.
Prolactin is a hormone, so named because it has a key role in milk production, however it also has over 300 other functions in the human body playing a key role in reproduction, metabolism, regulation of fluids, regulation of the immune system and influencing behavior.
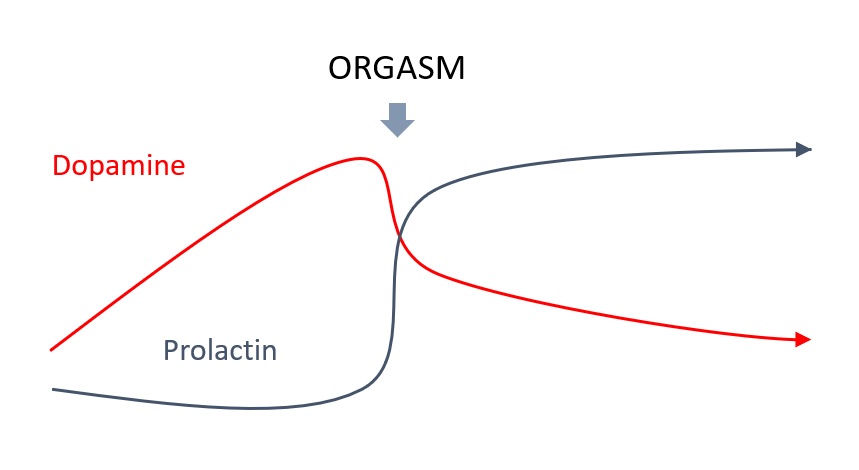
Dopamine and prolactin appear to move in opposite directions, when dopamine is high, prolactin is low, and vice versa. Prolactin is produced after orgasm and it has been suggested that it may be responsible for the sudden change in mood many men feel after ejaculation.
As Dopamine is the incentivization hormone, it drives the desire to have sex, once the prolactin is released, dopamine levels fall and all of a sudden, the man is left wondering where the desire came from in the first place. This relationship can be observed in the chart below.
One study showed that the ability for some men to achieve multiple orgasms, may be attributable to reduced prolactin production in those individuals (3). This suggests that blocking prolactin could allow the average man to also achieve such states. In comes Cabergoline.
Cabergoline
The drug Cabergoline blocks the release of prolactin and has been shown to increase erections and libido in men (4). In one study, 60 healthy males normally needed a break of 19 minutes between orgasms. After taking cabergoline, they were able to have several orgasms within a few minutes.
Cabergoline has also been reported to increase the intensity of male orgasms (5). Another study showed Cabergoline can be effective in increasing sex drive in both men and women, who are suffering from elevated levels of prolactin (6).
High doses of Cabergoline can have unwanted side effects, some studies have shown it can increase the risk of heart failure, however at normal doses the risk appears low (7). Also some level of prolactin is desirable as prolactin supports neurogenesis (growth in brain tissue) so blocking it completely for a long time period is not recommended.
Bromocriptine
Bromocriptine works in a similar way to Cabergoline. Bromocriptine stimulates dopamine production and simultaneously reduces the levels of prolactin, although not by as much as Cabergoline. Bromocriptine has been reported by many men and women to have a powerful impact on sex drive.
Bromocriptine has been shown to increase libido in men recovering from dialysis treatment (8). Bromocriptine was also shown to increase sex drive in women suffering from high levels of prolactin (9).
Like cabergoline, bromocriptine, especially in high doses can have unwanted side effects such as high blood pressure, seizure or stroke. It is not recommended to take any of these medications without the supervision of a doctor.
Mucuna Pruriens – a natural dopamine precursor
A safer alternative to increase levels of dopamine would be so use a natural supplement, such as Mucuna Pruriens.
Mucuna Pruriens, otherwise known as Velvet Bean is a tropical bean native to Africa and Asia. It has been used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat snake bites and Parkinson’s disease. The seeds of the plant contain between 3-6% L-Dopa. L-Dopa is a precursor to dopamine and has the advantage of being able to cross the blood-brain barrier, whereas dopamine cannot. Once L-Dopa has entered the central nervous system it is converted to dopamine. L-dopa supplementation is therefore more effective than direct supplementation with dopamine.
Mucuna Pruriens is widely sold as a supplement to increase motivation, improve mood and as an aphrodisiac. Unfortunately there is limited research on its effects on sex drive in humans however it has been shown to increase sexual behavior in male rats (10).
The Androgenic compounds
Androgens are natural or synthetic steroid hormones which regulate the development of male characteristics. Androgens are produced in the human body in the testes, ovaries and adrenal glands. The main androgen hormone in men is testosterone. Although testosterone is mainly thought of as a male sex hormone, women also produce testosterone although at lower levels.
Testosterone plays a critical role in libido and sexual arousal in both men and women. Testosterone levels are often lower in people who lead sedentary lifestyles, have poor diets or lack sleep. Testosterone levels also decline naturally with age. Testosterone supplementation has been shown to increase libido in men and women with suppressed testosterone levels (11) (12).
Testosterone is widely used in high doses in the bodybuilding community.
Direct supplementation of testosterone can lead to unwanted side effects such as acne, hair loss, deepening of voice, facial hair growth and in women enlargement of the clitoris – however these tend to only occur at higher doses such as those used for bodybuilding. In addition supplementing exogenous testosterone can inhibit the body’s natural production mechanism, making the problem of low testosterone worse once you stop supplementing.
Due to the side effects we would recommend avoiding direct supplementation with testosterone and rather suggest raising levels naturally through improved sleep, diet and exercise. If these factors alone aren’t sufficient you can try supplementing with Tribulus Terrestis or D-aspartic acid.
Tribulus Terrestis
Tribulus Terrestis is a small leafy plant which grows in Europe, Asia, Africa and the Middle East. The root and fruit of the plant have been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurvedic medicine for a variety of purposes, including increasing libido.
The jury is still out on how effective Tribulus is at increasing testosterone levels, however it has shown promise in some studies in women. One study of postmenopausal women with low libido found that supplementation with Tribulus over a 120 day period increased levels of testosterone and sexual desire (13). However other studies have not been able to back up these findings, especially in relation to the broader population (14).
D-aspartic acid
Another supplement which may be effective at increasing testosterone levels is D-aspartic acid. D-aspartic acid is a naturally occurring amino acid and it is important for brain and nerve development, as well as the development of testosterone.
However again the research findings are mixed. It seems D-aspartic acid is most effective at raising testosterone levels in non-resistance trained men (15). Studies in active resistance trained men found supplementation either had no effect or even reduced testosterone levels (16) (17) (18), therefore we would recommend supplementation only in individuals with suppressed testosterone levels and relatively inactive lifestyles.
There is no real research available on the efficacy of D-aspartic acid in women however as it works via stimulating the testes, it is unlikely to have the same effects for women.
Vasodilators
Another class of supplements works by increasing circulation, typically by increasing levels of nitric oxide. These compounds have less of an effect on sexual motivation but can improve erections in men and sensation in both men and women.
Nitric oxide (NO) is a molecule produced naturally in the body. NO is responsible for vasodilation, increased levels for NO cause the inner muscles of blood vessels to relax, which causes them to widen, thereby increasing circulation. The link between NO and erections is well established (19). Sildenafil (Viagra) works by inhibiting the enzyme which is responsible for breaking down NO in the genitals, thereby improving circulation in this area.
Viagra (Sildenafil) is a powerful vasodilator.
L-Citrulline
For anyone not wanting to take drugs such as Viagra another option is L-Citrulline. L-Citruline is an amino acid which is produced naturally in the body and is also found in various foods, including watermelon. L-Citriline has been shown to increase NO synthesis, thereby improving circulation (20). Supplementation with L-Citriline has been shown to improve erections in patients experiencing mild erectile dysfunction (21).
In conclusion
The causes of low libido can vary significantly from individual to individual, therefore no one treatment will work for everyone. The best approach is to ensure a healthy lifestyle with low stress, plenty of sleep and exercise and a healthy, balanced diet. For those looking for an additional boost a mixture of herbal remedies such as mucuna pruriens, Tribulus, D-aspartic acid and L-Citriline may help.
References
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2695750/
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7770195
3. https://www.nature.com/articles/3900823
4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14656205
5. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/1949087.stm
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29746287
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5240058/
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6357576
9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29475005
10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20456630
11. https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/91/7/2509/2656285
12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2673004/
13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27760089
14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26727646
15. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19860889
16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25844073
17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28841667
18. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24074738
19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8248281